Advantages and disadvantages of single-source dual-energy whole-body CT angiography with 50% reduced iodine dose at 40 keV reconstruction
- PMID: 33617294
- PMCID: PMC8506171
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20201276
Advantages and disadvantages of single-source dual-energy whole-body CT angiography with 50% reduced iodine dose at 40 keV reconstruction
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the feasibility of whole-body dual-energy computed tomographic angiography (DECTA) at 40 keV with 50% reduced iodine dose protocol.
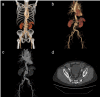
Methods: Whole-body CTA was performed in 65 patients; 31 of these patients underwent 120 kVp single-energy computed tomographic angiography (SECTA) with standard iodine dose (600 mgI/kg) and 34 with 40 keV DECTA with 50% reduced iodine dose (300 mgI/kg). SECTA data were reconstructed with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction of 40% (SECTA group), and DECTA data were reconstructed with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction of 40% (DECTA-40% group) and 80% (DECTA-80% group). CT numbers of the thoracic and abdominal aorta, iliac artery, background noise, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and arterial depiction were compared among the three groups. The CT dose index volumes (CTDIvol) for the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis were compared between SECTA and DECTA protocols.
Results: The vascular CT numbers and background noise were found to be significantly higher in DECTA groups than in the SECTA group (p < 0.001). SNR was significantly higher in the order corresponding to DECTA-80%, SECTA, and DECTA-40% (p < 0.001). The arterial depiction was comparable in almost all arteries; however, intrapelvic arterial depiction was significantly worse in DECTA groups than in the SECTA group (p < 0.0001-0.017). Unlike the pelvic region (p = 0.055), CTDIvol for the thorax (p < 0.0001) and abdomen (p = 0.0031) were significantly higher in the DECTA protocol than in the SECTA protocol.
Conclusion: DECTA at 40 keV with 50% reduced iodine dose provided higher vascular CT numbers and SNR than SECTA, and almost comparable arterial depiction, but had a degraded intrapelvic arterial depiction and required a larger radiation dose.
Advances in knowledge: DECTA enables 50% reduction of iodine dose while maintaining image quality, arterial depiction in almost all arteries, vascular CT numbers, and SNR; however, it does not allow clear visualization of intrapelvic arteries, requiring a slightly larger radiation dose compared with SECTA with standard iodine dose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Virtual Monochromatic Dual-Energy Aortoiliac CT Angiography With Reduced Iodine Dose: A Prospective Randomized Study.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019 Feb;212(2):467-474. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.19935. Epub 2018 Nov 26. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019. PMID: 30476460 Clinical Trial.
-
Optimized Bolus Threshold for Dual-Energy CT Angiography with Monoenergetic Images: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Radiology. 2021 Sep;300(3):615-623. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210102. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 34128721 Clinical Trial.
-
Deep-learning image-reconstruction algorithm for dual-energy CT angiography with reduced iodine dose: preliminary results.Clin Radiol. 2022 Feb;77(2):e138-e146. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2021.10.014. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Clin Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34782114
-
3D CT angiography.Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 2001 Feb;42(1):1-28. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 2001. PMID: 11244908 Review. No abstract available.
-
Review of Clinical Applications of Dual-Energy CT in Patients after Endovascular Aortic Repair.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 18;12(24):7766. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247766. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of post-processing images of abdominal CT small vessels using contrast enhancement boost technique: a retrospective study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Aug 1;15(8):6959-6968. doi: 10.21037/qims-2025-406. Epub 2025 Jul 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40785905 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of image quality, arterial depiction, and radiation dose between two rapid kVp-switching dual-energy CT scanners in CT angiography at 40-keV.Jpn J Radiol. 2023 Nov;41(11):1298-1307. doi: 10.1007/s11604-023-01448-5. Epub 2023 May 22. Jpn J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37212946 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Monoenergetic Imaging of Thoracoabdominal Computed Tomography Angiography on Photon-Counting Detector Computertomography: Assessment of Image Quality and Leveraging Low-keV Series for Salvaging Suboptimal Contrast Acquisitions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;14(24):2843. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242843. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767204 Free PMC article.
-
CT Angiography of the Aorta Using Photon-counting Detector CT with Reduced Contrast Media Volume.Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2023 Jan 26;5(1):e220140. doi: 10.1148/ryct.220140. eCollection 2023 Feb. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36860835 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation and iodine dose reduced thoraco-abdomino-pelvic dual-energy CT at 40 keV reconstructed with deep learning image reconstruction.Br J Radiol. 2022 Jun 1;95(1134):20211163. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20211163. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Br J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35230135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach S, Delgado V, Hausleiter J, Schoenhagen P, Min JK, Leipsic JA. SCCT expert consensus document on computed tomography imaging before transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI)/transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2012; 6: 366–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2012.11.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lehmkuhl L, Andres C, Lücke C, Foldyna B, Grothoff M, Scheinert D, et al. . Dynamic CT angiography after abdominal aortic endovascular aneurysm repair: differences in contrast agent dynamics in the aorta and endoleaks--preliminary results. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2012; 23: 744–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2012.02.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

