Circulating microparticles and activated platelets as novel prognostic biomarkers in COVID-19; relation to cancer
- PMID: 33617530
- PMCID: PMC7899358
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246806
Circulating microparticles and activated platelets as novel prognostic biomarkers in COVID-19; relation to cancer
Abstract
Background and aim: The study aimed to determine whether the MPs levels and platelet activation are affected by the COVID-19 infection in both malignant and non-malignant patients compared to healthy individuals and define their contribution to the COVID-19 associated coagulopathy and the relation of these MPs to other hematologic parameters.
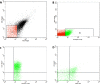
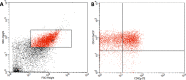
Patients and methods: We recruited 23 malignant patients with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) positive COVID-19, also, 19 COVID-19 non-malignant patients, and 20 healthy volunteers were also enrolled for comparison. Blood samples were collected from patients and healthy donors into 5 mL vacutainer tube containing 3.5% buffered sodium citrate solution for measurement of total microparticles (TMPs), platelet microparticles (PMPs), endothelial microparticles (EMPs), CD62 activated platelets, and CD41 platelet marker.
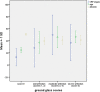
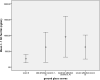
Results: COVID-19 malignant patients had significantly lower hemoglobin and platelets compared to COVID non-malignant ones, while they had significantly higher C-reactive protein, LDH, AST, Albunim, creatinine, and prognostic index (PI) compared to COVID-19 non-malignant patients. significant accumulations of TMPs, PMPs, EMPs, and activated platelets in COVID-19 affected patients compared to healthy controls. TMPs, and EMPs were significantly accumulated in COVID-19 malignant compared to COVID-19 non-malignant patients with no significant difference in PMPs between both.
Conclusion: Circulating MPs and activated platelets may be promising novel prognostic biomarkers capable of identifying potentially severe COVID-19 patients who require immediate care especially in cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Abid Hussein MN, Meesters EW, Osmanovic N, Romijn FP, Nieuwland R, Sturk A. Antigenic characterization of endothelial cell-derived microparticles and their detection ex vivo. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis: JTH. 2003;1(11):2434–43. Epub 2003/11/25. 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00455.x . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

