Effects of dynein inhibitor on the number of motor proteins transporting synaptic cargos
- PMID: 33617835
- PMCID: PMC8204214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.02.018
Effects of dynein inhibitor on the number of motor proteins transporting synaptic cargos
Abstract
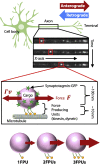
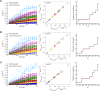
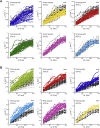
Synaptic cargo transport by kinesin and dynein in hippocampal neurons was investigated by noninvasively measuring the transport force based on nonequilibrium statistical mechanics. Although direct physical measurements such as force measurement using optical tweezers are difficult in an intracellular environment, the noninvasive estimations enabled enumerating force-producing units (FPUs) carrying a cargo comprising the motor proteins generating force. The number of FPUs served as a barometer for stable and long-distance transport by multiple motors, which was then used to quantify the extent of damage to axonal transport by dynarrestin, a dynein inhibitor. We found that dynarrestin decreased the FPU for retrograde transport more than for anterograde transport. This result indicates the applicability of the noninvasive force measurements. In the future, these measurements may be used to quantify damage to axonal transport resulting from neuronal diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases.
Copyright © 2021 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Number of kinesins engaged in axonal cargo transport: A novel biomarker for neurological disorders.Neurosci Res. 2023 Dec;197:25-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Neurosci Res. 2023. PMID: 37734449 Review.
-
Bidirectional, unlike unidirectional transport, allows transporting axonal cargos against their concentration gradient.J Theor Biol. 2022 Aug 7;546:111161. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2022.111161. Epub 2022 May 13. J Theor Biol. 2022. PMID: 35569529
-
Kinesin and dynein use distinct mechanisms to bypass obstacles.Elife. 2019 Sep 9;8:e48629. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48629. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31498080 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Localization of Cytoplasmic Dynein in Neurons Is Driven by Kinesin-1.Neuron. 2016 Jun 1;90(5):1000-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.046. Epub 2016 May 19. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27210554 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dynein-dynactin complex, kinesins, motor adaptors, and their phosphorylation in dendritogenesis.J Neurochem. 2020 Oct;155(1):10-28. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15010. Epub 2020 Apr 12. J Neurochem. 2020. PMID: 32196676 Review.
Cited by
-
Extreme-value analysis in nano-biological systems: applications and implications.Biophys Rev. 2024 Oct 2;16(5):571-579. doi: 10.1007/s12551-024-01239-w. eCollection 2024 Oct. Biophys Rev. 2024. PMID: 39618783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hirokawa N., Noda Y., Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:682–696. - PubMed
-
- Vale R.D. The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport. Cell. 2003;112:467–480. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama M., Higuchi H., Yanagida T. Chemomechanical coupling of the forward and backward steps of single kinesin molecules. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:790–797. - PubMed
-
- Okada Y., Higuchi H., Hirokawa N. Processivity of the single-headed kinesin KIF1A through biased binding to tubulin. Nature. 2003;424:574–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

