Trajectories of post-traumatic stress symptoms, anxiety, and depression in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A one-month follow-up
- PMID: 33618149
- PMCID: PMC7885629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2021.110399
Trajectories of post-traumatic stress symptoms, anxiety, and depression in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A one-month follow-up
Abstract
Objectives: Little is known about the mental health outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The aims of the study were: (1) to examine the trajectories of anxiety, depression, and pandemic-related stress factors (PRSF) of COVID-19 hospitalized patients one-month following hospitalization; (2) to assess the presence of post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) a month after hospitalization; (3) to identify baseline risk and protective factors that would predict PTSS one month after hospitalization.
Methods: We contacted hospitalized COVID-19 patients (n = 64) by phone, at three time-points: during the first days after admission to the hospital (T1); after ~two weeks from the beginning of hospitalization (T2), and one month after hospitalization (T3). At all time-points we assessed the levels of anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as PRSF. At T3, PTSS were assessed.
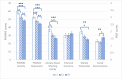
Results: The levels of depressive and anxiety symptoms decreased one-month following hospitalization. Moreover, higher levels of anxiety (standardized β = 1.15, 95% CI = 0.81-1.49, p < 0.001) and depression (β = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.63-1.31 p < 0.001) symptoms during the first week of hospitalization, feeling socially disconnected (β = 0.59, 95% CI = 0.37-0.81 p < 0.001) and experiencing a longer hospitalization period (β = 0.25, 95% CI = 0.03-0.47 p = 0.026) predicted higher PTSS scores a month post-hospitalization.
Conclusions: We identified early hospitalization risk factors for the development of PTSS one month after hospitalization that should be targeted to reduce the risk for PTSS.
Keywords: Anxiety; COVID-19; Depression; Mental health; PTSS; Patients.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Nie X.D., Wang Q., Wang M.N., Zhao S., Liu L., Zhu Y.L., Chen H. Anxiety and depression and its correlates in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2020:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Q., Hu C., Feng R., Yang Y. Investigation of the mental health of patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. Chin. J. Neurol. 2020;12
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

