Executive dysfunctions mediate between altered sensory processing and daily activity performance in older adults
- PMID: 33618664
- PMCID: PMC7898742
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02032-0
Executive dysfunctions mediate between altered sensory processing and daily activity performance in older adults
Abstract
Background: Sensory processing is essential for the interaction with the environment and for adequate daily function. Sensory processing may deteriorate with aging and restrict daily activity performance. Aging may also affect Executive functions (EFs) which are critical for daily activity performance. Yet, most studies refer separately to the impacts of sensory processing or EFs and use clinical evaluations that do not necessarily reflect functional restrictions in real life. This study aims to describe the prevalence of altered sensory processing in the elderly as expressed in daily life scenarios and explore whether EFs mediate between altered sensory processing and daily activity performance in older adults.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 167 healthy independently functioning people aged 65 and above who were living in the community, had sufficient cognitive status and no symptoms of depression (based on the GDS and the MMSE). All participants completed a socio-demographic-health questionnaire, the Adolescent/Adult Sensory Profile, the Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function-Adult Version and the Daily Living Questionnaire.
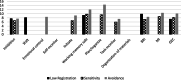
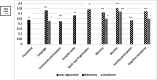
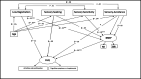
Results: Altered sensory processing, and mainly by the reduced ability to register and modulate sensory input from daily environment, were prevalent in older adults. Their impacts on daily activity performance were mediated by executive dysfunctions.
Conclusions: Executive dysfunctions may worsen the negative effects of altered sensory processing on daily activity performance in older adults. The interaction between EFs and sensory processing should receive growing attention in intervention and prevention programs for older adults, with the emphasis on their expressions and implications on peoples' function in real life context.
Keywords: Activities of daily living; Executive functions; Older adults; Sensory processing.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of sensory processing difficulties, cognitive impairment, and disease severity in predicting functional behavior among patients with multiple sclerosis.Disabil Rehabil. 2021 Apr;43(8):1129-1136. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2019.1653998. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Disabil Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 31453721
-
Untreated if unrecognized: A cognitive profile of sustained subjective executive dysfunctions in COVID-19.Appl Neuropsychol Adult. 2025 Jul-Aug;32(4):903-913. doi: 10.1080/23279095.2023.2223329. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Appl Neuropsychol Adult. 2025. PMID: 37334922
-
Executive function subcomponents and their relations to everyday functioning in healthy older adults.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2016 Oct;38(8):925-40. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2016.1177490. Epub 2016 May 20. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2016. PMID: 27206842 Free PMC article.
-
The involvement of altered sensory modulation in neurological conditions and its relevance to neuro-rehabilitation: a narrative literature review.Disabil Rehabil. 2021 Aug;43(17):2511-2520. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2019.1699175. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Disabil Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 31829745 Review.
-
Assessment of cognitive instrumental activities of daily living: a systematic review.Disabil Rehabil. 2021 May;43(10):1342-1358. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2019.1665720. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Disabil Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 31549907
Cited by
-
Relationships between executive functions and sensory patterns among adults with specific learning disabilities as reflected in their daily functioning.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 7;17(4):e0266385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266385. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35390062 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Visual Exploration through Augmented Gaze: High Acceptance of Immersive Virtual Biking by Oldest Olds.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 17;20(3):1671. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031671. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767037 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Co-Regulation-Related Factors in the Mothers of ADHD Children-Proof of Concept Study.Children (Basel). 2023 Jul 26;10(8):1286. doi: 10.3390/children10081286. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628285 Free PMC article.
-
Higher levels of neuroticism in older adults predict lower executive functioning across time: the mediating role of perceived stress.Eur J Ageing. 2021 Dec 16;19(3):633-649. doi: 10.1007/s10433-021-00665-z. eCollection 2022 Sep. Eur J Ageing. 2021. PMID: 36052201 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Processing Abnormalities in Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Cognitive Impairment: A Mixed Methods Study.Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2022 Jan 8;8:23337214211068290. doi: 10.1177/23337214211068290. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2022. PMID: 35024382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Engel-Yeger B. The involvement of altered sensory modulation in neurological conditions and its relevance to neuro-rehabilitation: a narrative literature review. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;12:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Dunn W. The sensory profile: Examiner’s manual. Psychological. 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

