Emerging Therapeutic Applications for Fumarates
- PMID: 33618840
- PMCID: PMC7954891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.01.004
Emerging Therapeutic Applications for Fumarates
Abstract
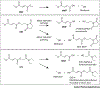
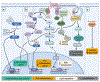
Fumarates are successfully used for the treatment of psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Their antioxidative, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective properties make fumarates attractive therapeutic candidates for other pathologies. The exact working mechanisms of fumarates are, however, not fully understood. Further elucidation of the mechanisms is required if these drugs are to be successfully repurposed for other diseases. Towards this, administration route, dosage, and treatment timing, frequency, and duration are important parameters to consider and optimize with clinical paradigms in mind. Here, we summarize the rapidly expanding literature on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of fumarates, including a discussion on two recently FDA-approved fumarates VumerityTM and BafiertamTM. We review emerging applications of fumarates, focusing on neurological and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; fumarates; ischemia-reperfusion injury; neurodegenerative disease; neuropathic pain.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests Drs Grace, Abell, and Avery receive funding from Biogen Inc. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) - EMA (2011) Assessment report on Fumaria officinalis L., herba, EMA.
-
- Schweckendiek W (1959) [Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris]. Med. Monatsschr 13, 103–4 - PubMed
-
- Schimrigk S et al. (2006) Oral fumaric acid esters for the treatment of active multiple sclerosis: An open-label, baseline-controlled pilot study. Eur. J. Neurol 13, 604–610 - PubMed
-
- Meissner M et al. (2012) Dimethyl fumarate - Only an anti-psoriatic medication? JDDG - J. Ger. Soc. Dermatology 10, 793–801 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

