Real-time measurements of aminoglycoside effects on protein synthesis in live cells
- PMID: 33619089
- PMCID: PMC7936356
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2013315118
Real-time measurements of aminoglycoside effects on protein synthesis in live cells
Abstract
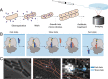
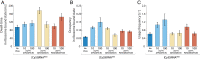
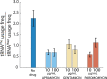
The spread of antibiotic resistance is turning many of the currently used antibiotics less effective against common infections. To address this public health challenge, it is critical to enhance our understanding of the mechanisms of action of these compounds. Aminoglycoside drugs bind the bacterial ribosome, and decades of results from in vitro biochemical and structural approaches suggest that these drugs disrupt protein synthesis by inhibiting the ribosome's translocation on the messenger RNA, as well as by inducing miscoding errors. So far, however, we have sparse information about the dynamic effects of these compounds on protein synthesis inside the cell. In the present study, we measured the effect of the aminoglycosides apramycin, gentamicin, and paromomycin on ongoing protein synthesis directly in live Escherichia coli cells by tracking the binding of dye-labeled transfer RNAs to ribosomes. Our results suggest that the drugs slow down translation elongation two- to fourfold in general, and the number of elongation cycles per initiation event seems to decrease to the same extent. Hence, our results imply that none of the drugs used in this study cause severe inhibition of translocation.
Keywords: antibiotics; single-molecule tracking; superresolution microscopy; tRNA; translation.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-function comparison of Arbekacin with other aminoglycosides elucidates its higher potency as bacterial translation inhibitor.Sci Rep. 2025 May 25;15(1):18271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02391-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40415027 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Measurements of Erythromycin's Effect on Protein Synthesis Kinetics in Living Bacterial Cells.J Mol Biol. 2021 May 14;433(10):166942. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166942. Epub 2021 Mar 18. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33744313
-
Translation error clusters induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 23;12(1):1830. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21942-6. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33758186 Free PMC article.
-
Improving on nature: antibiotics that target the ribosome.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Oct;8(5):534-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.08.004. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16111914 Review.
-
Antibiotics and compounds affecting tanslation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Specific enhancement of aminoacyl-tRNA binding by methylaxnthines.Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;10(2):97-122. doi: 10.1007/BF01742203. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976. PMID: 768741 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic insights into translation inhibition by aminoglycoside antibiotic arbekacin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 9;49(12):6880-6892. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab495. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34125898 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function comparison of Arbekacin with other aminoglycosides elucidates its higher potency as bacterial translation inhibitor.Sci Rep. 2025 May 25;15(1):18271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02391-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40415027 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural and morphological studies on variables affecting Escherichia coli with selected commercial antibiotics.Cell Surf. 2024 Jan 14;11:100120. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2024.100120. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cell Surf. 2024. PMID: 38313869 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Fidelity during Bacterial Stresses and Host Interactions.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 28;12(3):383. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12030383. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36986305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal kinetics of the SRP pathway in live E. coli cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 20;119(38):e2204038119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204038119. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36095178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson D. N., Ribosome-targeting antibiotics and mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 12, 35–48 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Becker B., Cooper M. A., Aminoglycoside antibiotics in the 21st century. ACS Chem. Biol. 8, 105–115 (2013). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization , “Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine, 6th revision” (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

