HIF-1α-induced expression of m6A reader YTHDF1 drives hypoxia-induced autophagy and malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting ATG2A and ATG14 translation
- PMID: 33619246
- PMCID: PMC7900110
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00453-8
HIF-1α-induced expression of m6A reader YTHDF1 drives hypoxia-induced autophagy and malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting ATG2A and ATG14 translation
Abstract
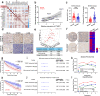
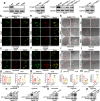
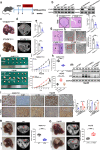
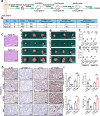
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), and its reader protein YTHDF1, play a pivotal role in human tumorigenesis by affecting nearly every stage of RNA metabolism. Autophagy activation is one of the ways by which cancer cells survive hypoxia. However, the possible involvement of m6A modification of mRNA in hypoxia-induced autophagy was unexplored in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, specific variations in YTHDF1 expression were detected in YTHDF1-overexpressing, -knockout, and -knockdown HCC cells, HCC organoids, and HCC patient-derived xenograft (PDX) murine models. YTHDF1 expression and hypoxia-induced autophagy were significantly correlated in vitro; significant overexpression of YTHDF1 in HCC tissues was associated with poor prognosis. Multivariate cox regression analysis identified YTHDF1 expression as an independent prognostic factor in patients with HCC. Multiple HCC models confirmed that YTHDF1 deficiency inhibited HCC autophagy, growth, and metastasis. Luciferase reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated that HIF-1α regulated YTHDF1 transcription by directly binding to its promoter region under hypoxia. The results of methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing, proteomics, and polysome profiling indicated that YTHDF1 contributed to the translation of autophagy-related genes ATG2A and ATG14 by binding to m6A-modified ATG2A and ATG14 mRNA, thus facilitating autophagy and autophagy-related malignancy of HCC. Taken together, HIF-1α-induced YTHDF1 expression was associated with hypoxia-induced autophagy and autophagy-related HCC progression via promoting translation of autophagy-related genes ATG2A and ATG14 in a m6A-dependent manner. Our findings suggest that YTHDF1 is a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for patients with HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HIF-1α-induced expression of the m6A reader YTHDF1 inhibits the ferroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells by promoting SLC7A11 translation.Aging Cell. 2024 Sep;23(9):e14210. doi: 10.1111/acel.14210. Epub 2024 May 23. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38783692 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine Reader YTHDF1 Promotes Stemness and Therapeutic Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Enhancing NOTCH1 Expression.Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 15;84(6):827-840. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1916. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38241695
-
HBXIP drives metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via METTL3-mediated m6A modification of HIF-1α.J Cell Physiol. 2021 May;236(5):3863-3880. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30128. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33305825
-
The functional roles, cross-talk and clinical implications of m6A modification and circRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jul 22;17(12):3059-3079. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62767. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34421350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression with susceptibility to hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2023 Dec;38(3-4):149-158. doi: 10.1177/03936155231204391. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Int J Biol Markers. 2023. PMID: 37787154 Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal profile, levels of aflatoxin M1, exposure, and the risk characterization of local cheese 'wagashi' consumed in the Ho Municipality, Volta Region, Ghana.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Jan 17;12:186-199. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.01.009. eCollection 2024 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38313814 Free PMC article.
-
USP24 promotes autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing the K48-linked ubiquitination of Beclin1.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 8;7(1):1279. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06999-5. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39379617 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC2 promotes autophagy-associated HCC malignant progression by transcriptionally activating LAPTM4B.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 15;15(8):593. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06981-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39147759 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 28;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01321-4. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36707507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The YTHDF1-TRAF6 pathway regulates the neuroinflammatory response and contributes to morphine tolerance and hyperalgesia in the periaqueductal gray.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Dec 22;19(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02672-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36550542 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

