Causal role for sleep-dependent reactivation of learning-activated sensory ensembles for fear memory consolidation
- PMID: 33619256
- PMCID: PMC7900186
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21471-2
Causal role for sleep-dependent reactivation of learning-activated sensory ensembles for fear memory consolidation
Abstract
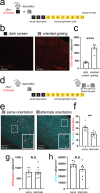
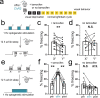
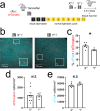
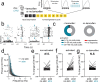
Learning-activated engram neurons play a critical role in memory recall. An untested hypothesis is that these same neurons play an instructive role in offline memory consolidation. Here we show that a visually-cued fear memory is consolidated during post-conditioning sleep in mice. We then use TRAP (targeted recombination in active populations) to genetically label or optogenetically manipulate primary visual cortex (V1) neurons responsive to the visual cue. Following fear conditioning, mice respond to activation of this visual engram population in a manner similar to visual presentation of fear cues. Cue-responsive neurons are selectively reactivated in V1 during post-conditioning sleep. Mimicking visual engram reactivation optogenetically leads to increased representation of the visual cue in V1. Optogenetic inhibition of the engram population during post-conditioning sleep disrupts consolidation of fear memory. We conclude that selective sleep-associated reactivation of learning-activated sensory populations serves as a necessary instructive mechanism for memory consolidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optogenetic reactivation of memory ensembles in the retrosplenial cortex induces systems consolidation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 23;116(17):8576-8581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818432116. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30877252 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neurons' cytosolic and membrane-bound ribosomal transcript profiles are differentially regulated by learning and subsequent sleep.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 30;118(48):e2108534118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108534118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34819370 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep supports cued fear extinction memory consolidation independent of circadian phase.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Jul;132:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27109918
-
Inception of a false memory by optogenetic manipulation of a hippocampal memory engram.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 2;369(1633):20130142. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0142. Print 2014 Jan 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24298144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sculpting memory during sleep: concurrent consolidation and forgetting.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017 Jun;44:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2017.02.012. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28278432 Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive neuroscience perspective on memory: overview and summary.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Jul 26;17:1217093. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1217093. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37565054 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylcholine-gated current translates wake neuronal firing rate information into a spike timing-based code in Non-REM sleep, stabilizing neural network dynamics during memory consolidation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Sep 20;17(9):e1009424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009424. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34543284 Free PMC article.
-
Brief sleep disruption alters synaptic structures among hippocampal and neocortical somatostatin-expressing interneurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 5:2024.07.22.604591. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.22.604591. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Sleep. 2025 Jun 13;48(6):zsaf064. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaf064. PMID: 39211205 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Sevoflurane-induced amnesia is associated with inhibition of hippocampal cell ensemble activity after learning.Biol Open. 2022 Dec 15;11(12):bio059666. doi: 10.1242/bio.059666. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Biol Open. 2022. PMID: 36541652 Free PMC article.
-
Contextual Fear Learning and Extinction in the Primary Visual Cortex of Mice.Neurosci Bull. 2023 Jan;39(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00889-8. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 35704211 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

