Life-long brain compensatory responses to galactic cosmic radiation exposure
- PMID: 33619310
- PMCID: PMC7900210
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83447-y
Life-long brain compensatory responses to galactic cosmic radiation exposure
Abstract
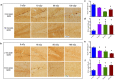
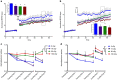
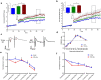
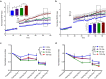
Galactic cosmic radiation (GCR) composed of high-energy, heavy particles (HZE) poses potentially serious hazards to long-duration crewed missions in deep space beyond earth's magnetosphere, including planned missions to Mars. Chronic effects of GCR exposure on brain structure and cognitive function are poorly understood, thereby limiting risk reduction and mitigation strategies to protect against sequelae from exposure during and after deep-space travel. Given the selective vulnerability of the hippocampus to neurotoxic insult and the importance of this brain region to learning and memory, we hypothesized that GCR-relevant HZE exposure may induce long-term alterations in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and hippocampal-dependent learning and memory. To test this hypothesis, we irradiated 3-month-old male and female mice with a single, whole-body dose of 10, 50, or 100 cGy 56Fe ions (600 MeV, 181 keV/μm) at Brookhaven National Laboratory. Our data reveal complex, dynamic, time-dependent effects of HZE exposure on the hippocampus. Two months post exposure, neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and learning were impaired compared to sham-irradiated, age-matched controls. By six months post-exposure, deficits in spatial learning were absent in irradiated mice, and synaptic potentiation was enhanced. Enhanced performance in spatial learning and facilitation of synaptic plasticity in irradiated mice persisted 12 months post-exposure, concomitant with a dramatic rebound in adult-born neurons. Synaptic plasticity and spatial learning remained enhanced 20 months post-exposure, indicating a life-long influence on plasticity and cognition from a single exposure to HZE in young adulthood. These findings suggest that GCR-exposure can persistently alter brain health and cognitive function during and after long-duration travel in deep space.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole-Body Exposure to 28Si-Radiation Dose-Dependently Disrupts Dentate Gyrus Neurogenesis and Proliferation in the Short Term and New Neuron Survival and Contextual Fear Conditioning in the Long Term.Radiat Res. 2017 Nov;188(5):532-551. doi: 10.1667/RR14797.1. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Radiat Res. 2017. PMID: 28945526 Free PMC article.
-
The longitudinal behavioral effects of acute exposure to galactic cosmic radiation in female C57BL/6J mice: Implications for deep space missions, female crews, and potential antioxidant countermeasures.J Neurochem. 2025 Jan;169(1):e16225. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16225. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39318241 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic HDAC3 inhibition ameliorates impairments in synaptic plasticity caused by simulated galactic cosmic radiation exposure in male mice.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021 Feb;178:107367. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2020.107367. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021. PMID: 33359392 Free PMC article.
-
Getting ready for the manned mission to Mars: the astronauts' risk from space radiation.Naturwissenschaften. 2007 Jul;94(7):517-26. doi: 10.1007/s00114-006-0204-0. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Naturwissenschaften. 2007. PMID: 17235598 Review.
-
Microglia: Ally and Enemy in Deep Space.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Jul;126:509-514. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.03.036. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 33862064 Review.
Cited by
-
Ionizing radiation, cerebrovascular disease, and consequent dementia: A review and proposed framework relevant to space radiation exposure.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 25;13:1008640. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1008640. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36388106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Sex- and Genotype-Specific Effects of 56Fe Irradiation on Wild-Type and APPswe/PS1dE9 Transgenic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 10;22(24):13305. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413305. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948098 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-biased effects on hippocampal circuit development by perinatal SERT expression in CA3 pyramidal neurons.Development. 2022 Nov 1;149(21):dev200549. doi: 10.1242/dev.200549. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Development. 2022. PMID: 36178075 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Impact of Social Isolation and Space Radiation on Behavior and Motor Learning in Rats.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 18;13(3):826. doi: 10.3390/life13030826. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983981 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-scale simulation of neuronal damage by galactic cosmic rays.Phys Med Biol. 2022 Nov 25;67(23):10.1088/1361-6560/ac95f4. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac95f4. Phys Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36172820 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

