Social distance monitoring framework using deep learning architecture to control infection transmission of COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33619448
- PMCID: PMC7889035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.102777
Social distance monitoring framework using deep learning architecture to control infection transmission of COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
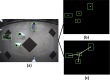
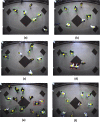
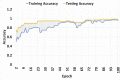
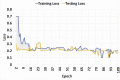
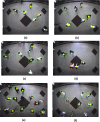
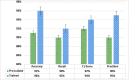
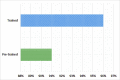
The recent outbreak of the COVID-19 affected millions of people worldwide, yet the rate of infected people is increasing. In order to cope with the global pandemic situation and prevent the spread of the virus, various unprecedented precaution measures are adopted by different countries. One of the crucial practices to prevent the spread of viral infection is social distancing. This paper intends to present a social distance framework based on deep learning architecture as a precautionary step that helps to maintain, monitor, manage, and reduce the physical interaction between individuals in a real-time top view environment. We used Faster-RCNN for human detection in the images. As the human's appearance significantly varies in a top perspective; therefore, the architecture is trained on the top view human data set. Moreover, taking advantage of transfer learning, a new trained layer is fused with a pre-trained architecture. After detection, the pair-wise distance between peoples is estimated in an image using Euclidean distance. The detected bounding box's information is utilized to measure the central point of an individual detected bounding box. A violation threshold is defined that uses distance to pixel information and determines whether two people violate social distance or not. Experiments are conducted using various test images; results demonstrate that the framework effectively monitors the social distance between peoples. The transfer learning technique enhances the overall performance of the framework by achieving an accuracy of 96% with a False Positive Rate of 0.6%.
Keywords: COVID-19; Deep learning; Faster-RCNN; Internet of things; Person detection; Social distancing; Top view; Transfer learning.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A deep learning-based social distance monitoring framework for COVID-19.Sustain Cities Soc. 2021 Feb;65:102571. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102571. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Sustain Cities Soc. 2021. PMID: 33163330 Free PMC article.
-
Real time deep learning framework to monitor social distancing using improved single shot detector based on overhead position.Earth Sci Inform. 2022;15(1):585-602. doi: 10.1007/s12145-021-00758-4. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Earth Sci Inform. 2022. PMID: 35035588 Free PMC article.
-
An Automatic System to Monitor the Physical Distance and Face Mask Wearing of Construction Workers in COVID-19 Pandemic.SN Comput Sci. 2022;3(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s42979-021-00894-0. Epub 2021 Oct 29. SN Comput Sci. 2022. PMID: 34729498 Free PMC article.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
Deep visual social distancing monitoring to combat COVID-19: A comprehensive survey.Sustain Cities Soc. 2022 Oct;85:104064. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.104064. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Sustain Cities Soc. 2022. PMID: 35880102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developments in Image Processing Using Deep Learning and Reinforcement Learning.J Imaging. 2023 Sep 30;9(10):207. doi: 10.3390/jimaging9100207. J Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37888314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The case of Tehran's urban heat island, Iran: Impacts of urban 'lockdown' associated with the COVID-19 pandemic.Sustain Cities Soc. 2021 Dec;75:103263. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103263. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Sustain Cities Soc. 2021. PMID: 36568531 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a real-time social distancing detection system based on YOLOv4-tiny and bird-eye view for COVID-19.J Real Time Image Process. 2022;19(3):551-563. doi: 10.1007/s11554-022-01203-5. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Real Time Image Process. 2022. PMID: 35222727 Free PMC article.
-
An embedded toolset for human activity monitoring in critical environments.Expert Syst Appl. 2022 Aug 1;199:117125. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117125. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Expert Syst Appl. 2022. PMID: 35431465 Free PMC article.
-
An Optimized Deep Learning Approach for the Prediction of Social Distance Among Individuals in Public Places During Pandemic.New Gener Comput. 2023;41(1):135-154. doi: 10.1007/s00354-022-00202-1. Epub 2023 Jan 2. New Gener Comput. 2023. PMID: 36620356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolph C., Amano K., Bang-Jensen B., Fullman N., Wilkerson J. medRxiv. 2020 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M., Ahmed I., Khan F.A., Qayum F., Aljuaid H. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks. 2020;16 1550147720934738.
-
- Ahmad M., Ahmed I., Ullah K., Khan I., Adnan A. 2018 9th IEEE annual ubiquitous computing, electronics mobile communication conference (UEMCON) (pp. 746–752). doi:10.1109/UEMCON.2018.8796595.
-
- Ahmed I., Adnan A. Cluster Computing. 2017:1–22.
-
- Ahmed I., Ahmad A., Piccialli F., Sangaiah A.K., Jeon G. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2018;5:1598–1605.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
