This is a preprint.
SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 sensitivity to mRNA vaccine-elicited, convalescent and monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 33619509
- PMCID: PMC7899479
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.01.19.21249840
SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 sensitivity to mRNA vaccine-elicited, convalescent and monoclonal antibodies
Update in
-
Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 to mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies.Nature. 2021 May;593(7857):136-141. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03412-7. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33706364 Free PMC article.
Abstract
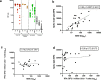
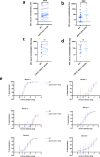
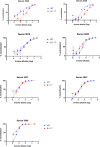
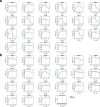
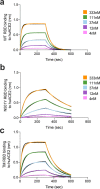
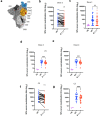
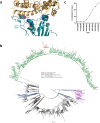
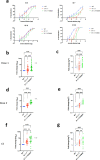
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission is uncontrolled in many parts of the world, compounded in some areas by higher transmission potential of the B1.1.7 variant now seen in 50 countries. It is unclear whether responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines based on the prototypic strain will be impacted by mutations found in B.1.1.7. Here we assessed immune responses following vaccination with mRNA-based vaccine BNT162b2. We measured neutralising antibody responses following a single immunization using pseudoviruses expressing the wild-type Spike protein or the 8 amino acid mutations found in the B.1.1.7 spike protein. The vaccine sera exhibited a broad range of neutralising titres against the wild-type pseudoviruses that were modestly reduced against B.1.1.7 variant. This reduction was also evident in sera from some convalescent patients. Decreased B.1.1.7 neutralisation was also observed with monoclonal antibodies targeting the N-terminal domain (9 out of 10), the Receptor Binding Motif (RBM) (5 out of 31), but not in neutralising mAbs binding outside the RBM. Introduction of the E484K mutation in a B.1.1.7 background to reflect newly emerging viruses in the UK led to a more substantial loss of neutralising activity by vaccine-elicited antibodies and mAbs (19 out of 31) over that conferred by the B.1.1.7 mutations alone. E484K emergence on a B.1.1.7 background represents a threat to the vaccine BNT162b.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; mutation; neutralising antibodies; vaccine; variant.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests A.D.M., J.B., D.P., C.S.F., S.B., K.C., N.S., E.C., G.S., S.J., A.L., H.W.V., M.S.P., L.P. and D.C. are employees of Vir Biotechnology and may hold shares in Vir Biotechnology. H.W.V. is a founder of PierianDx and Casma Therapeutics. Neither company provided funding for this work or is performing related work. D.V. is a consultant for Vir Biotechnology Inc. The Veesler laboratory has received a sponsored research agreement from Vir Biotechnology Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. RKG has received consulting fees from UMOVIS Lab, Gilead and ViiV.
Figures




References
-
- Davies N. G. et al. Estimated transmissibility and severity of novel SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern 202012/01 in England. medRxiv, 2020.2012.2024.20248822, doi:10.1101/2020.12.24.20248822 (2020). - DOI
-
- Volz E. et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Lineage B.1.1.7 in England: Insights from linking epidemiological and genetic data. medRxiv, 2020.2012.2030.20249034, doi:10.1101/2020.12.30.20249034 (2021). - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
