Lipoteichoic acid from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1: a novel postbiotic that reduces fat deposition via IGF-1 pathway
- PMID: 33620143
- PMCID: PMC8913875
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13769
Lipoteichoic acid from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1: a novel postbiotic that reduces fat deposition via IGF-1 pathway
Abstract
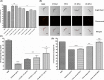
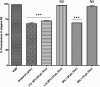
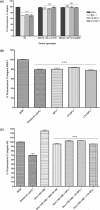
Obesity and its related metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, are major risk factors for morbidity and mortality in the world population. In this context, supplementation with the probiotic strain Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1 (CECT8145) has been shown to ameliorate obesity biomarkers. Analyzing the basis of this observation and using the pre-clinical model Caenorhabditis elegans, we have found that lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of BPL1 is responsible for its fat-reducing properties and that this attribute is preserved under hyperglycaemic conditions. This fat-reducing capacity of both BPL1 and LTA-BPL1 is abolished under glucose restriction, as a result of changes in LTA chemical composition. Moreover, we have demonstrated that LTA exerts this function through the IGF-1 pathway, as does BPL1 strain. These results open the possibility of using LTA as a novel postbiotic, whose beneficial properties can be applied therapeutically and/or preventively in metabolic syndrome and diabetes-related disorders.
© 2021 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1™ and Its Lipoteichoic Acid Modulate Longevity and Improve Age/Stress-Related Behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 13;12(12):2107. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122107. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136226 Free PMC article.
-
An Infant Milk Formula Supplemented with Heat-Treated Probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CECT 8145, Reduces Fat Deposition in C. elegans and Augments Acetate and Lactate in a Fermented Infant Slurry.Foods. 2020 May 19;9(5):652. doi: 10.3390/foods9050652. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32438563 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis (BPL1) Supplementation in Children and Adolescents with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Randomized Crossover Trial.Nutrients. 2020 Oct 13;12(10):3123. doi: 10.3390/nu12103123. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33066107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro Cholesterol Assimilation by Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis (BPL1) Probiotic Bacteria Under Intestinal Conditions.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2022;22(4):433-439. doi: 10.2174/1871530321666210908124848. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34496737 Review.
-
Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis 420 for Metabolic Health: Review of the Research.Nutrients. 2020 Mar 25;12(4):892. doi: 10.3390/nu12040892. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32218248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential role of gut microbiota-derived metabolites as regulators of metabolic syndrome-associated mitochondrial and endolysosomal dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Aug;56(8):1691-1702. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01282-3. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39085351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans as a Screening Model for Probiotics with Properties against Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):1321. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021321. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of the Intestinal Microorganisms in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients: Effects of Smoking.ACS Omega. 2022 Jan 5;7(2):1628-1638. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02120. eCollection 2022 Jan 18. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35071858 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: An update for 2021-2022.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025 May-Jun;44(3):213-453. doi: 10.1002/mas.21873. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025. PMID: 38925550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postbiotics: an insightful review of the latest category in functional biotics.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 2;41(8):293. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04483-8. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40751848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amat‐Bou, M. , Garcia‐Ribera, S. , Climent, E. , Piquer‐Garcia, I. , Corripio, R. , Sanchez‐Infantes, D. , et al. (2020) Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis (BPL1) Supplementation in children and adolescents with Prader‐Willi syndrome: a randomized crossover trial. Nutrients 12: 3123. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashrafi, K. , Chang, F.Y. , Watts, J.L. , Fraser, A.G. , Kamath, R.S. , Ahringer, J. , and Ruvkun, G. (2003) Genome‐wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulatory genes. Nature 421: 268–272. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri, M. , Bonafe, M. , Franceschi, C. , and Paolisso, G. (2003) Insulin/IGF‐I‐signaling pathway: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of longevity from yeast to humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285: E1064–E1071. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

