Lipoteichoic acid from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1: a novel postbiotic that reduces fat deposition via IGF-1 pathway
- PMID: 33620143
- PMCID: PMC8913875
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13769
Lipoteichoic acid from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1: a novel postbiotic that reduces fat deposition via IGF-1 pathway
Abstract
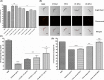
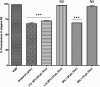
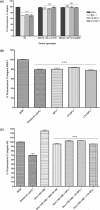
Obesity and its related metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, are major risk factors for morbidity and mortality in the world population. In this context, supplementation with the probiotic strain Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BPL1 (CECT8145) has been shown to ameliorate obesity biomarkers. Analyzing the basis of this observation and using the pre-clinical model Caenorhabditis elegans, we have found that lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of BPL1 is responsible for its fat-reducing properties and that this attribute is preserved under hyperglycaemic conditions. This fat-reducing capacity of both BPL1 and LTA-BPL1 is abolished under glucose restriction, as a result of changes in LTA chemical composition. Moreover, we have demonstrated that LTA exerts this function through the IGF-1 pathway, as does BPL1 strain. These results open the possibility of using LTA as a novel postbiotic, whose beneficial properties can be applied therapeutically and/or preventively in metabolic syndrome and diabetes-related disorders.
© 2021 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Amat‐Bou, M. , Garcia‐Ribera, S. , Climent, E. , Piquer‐Garcia, I. , Corripio, R. , Sanchez‐Infantes, D. , et al. (2020) Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis (BPL1) Supplementation in children and adolescents with Prader‐Willi syndrome: a randomized crossover trial. Nutrients 12: 3123. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashrafi, K. , Chang, F.Y. , Watts, J.L. , Fraser, A.G. , Kamath, R.S. , Ahringer, J. , and Ruvkun, G. (2003) Genome‐wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulatory genes. Nature 421: 268–272. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri, M. , Bonafe, M. , Franceschi, C. , and Paolisso, G. (2003) Insulin/IGF‐I‐signaling pathway: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of longevity from yeast to humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285: E1064–E1071. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

