OsmiR396/growth regulating factor modulate rice grain size through direct regulation of embryo-specific miR408
- PMID: 33620493
- PMCID: PMC8154042
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiab084
OsmiR396/growth regulating factor modulate rice grain size through direct regulation of embryo-specific miR408
Abstract
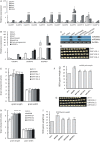
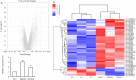
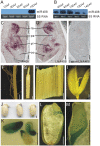
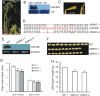
microRNAs (miRNAs) are promising targets for crop improvement of complex agricultural traits. Coordinated activity between/among different miRNAs may fine-tune specific developmental processes in diverse organisms. Grain size is a main factor determining rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop yield, but the network of miRNAs influencing this trait remains uncharacterized. Here we show that sequestering OsmiR396 through target mimicry (MIM396) can substantially increase grain size in several japonica and indica rice subspecies and in plants with excessive tillers and a high panicle density. Thus, OsmiR396 has a major role related to the regulation of rice grain size. The grain shape of Growth Regulating Factor8 (OsGRF8)-overexpressing transgenic plants was most similar to that of MIM396 plants, suggesting OsGRF8 is a major mediator of OsmiR396 in grain size regulation. A miRNA microarray analysis revealed changes to the expression of many miRNAs, including OsmiR408, in the MIM396 plants. Analyses of gene expression patterns and functions indicated OsmiR408 is an embryo-specific miRNA that positively regulates grain size. Silencing OsmiR408 expression (miR408KO) using CRISPR technology resulted in small grains. Moreover, we revealed the direct regulatory effects of OsGRF8 on OsMIR408 expression. A genetic analysis further showed that the large-grain phenotype of MIM396 plants could be complemented by miR408KO. Also, several hormone signaling pathways might be involved in the OsmiR396/GRF-meditated grain size regulation. Our findings suggest that genetic regulatory networks comprising various miRNAs, such as OsmiR396 and OsmiR408, may be crucial for controlling rice grain size. Furthermore, the OsmiR396/GRF module may be important for breeding new high-yielding rice varieties.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The OsmiR396-OsGRF8-OsF3H-flavonoid pathway mediates resistance to the brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa).Plant Biotechnol J. 2019 Aug;17(8):1657-1669. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13091. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30734457 Free PMC article.
-
miR1432-OsACOT (Acyl-CoA thioesterase) module determines grain yield via enhancing grain filling rate in rice.Plant Biotechnol J. 2019 Apr;17(4):712-723. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13009. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30183128 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice.Nat Plants. 2015 Dec 21;2:15203. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2015.203. Nat Plants. 2015. PMID: 27250749
-
The molecular mechanism of transcription factor regulation of grain size in rice.Plant Sci. 2025 May;354:112434. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2025.112434. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40023197 Review.
-
Molecular insights into the regulation of rice kernel elongation.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019 Nov;39(7):904-923. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2019.1632257. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31303070 Review.
Cited by
-
QTL analysis of traits related to seed size and shape in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.).PLoS One. 2023 Nov 2;18(11):e0293155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293155. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37917626 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs and their role in plants: prospective omics-tools for improving growth, development and stress tolerance in field crops.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 20;52(1):249. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10305-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39976851 Review.
-
Fine mapping and characterization of a major QTL for grain weight on wheat chromosome arm 5DL.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Sep;135(9):3237-3246. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04182-0. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 35904627
-
TaMIR397-6A and -6B Homoeologs Encode Active miR397 Contributing to the Regulation of Grain Size in Hexaploid Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 13;25(14):7696. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147696. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062941 Free PMC article.
-
Riboflavin mediates m6A modification targeted by miR408, promoting early somatic embryogenesis in longan.Plant Physiol. 2023 Jul 3;192(3):1799-1820. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad139. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36930572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armenta-Medina A, Lepe-Soltero D, Xiang D, Datla R, Abreu-Goodger C, Gillmor CS (2017) Arabidopsis thaliana miRNAs promote embryo pattern formation beginning in the zygote. Dev Biol 431: 145–151 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Che R, Tong H, Shi B, Liu Y, Fang S, Liu D, Xiao Y, Hu B, Liu L, Wang H, et al. (2015) Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat Plants 2: 15195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

