Paraventricular Nucleus P2X7 Receptors Aggravate Acute Myocardial Infarction Injury via ROS-Induced Vasopressin-V1b Activation in Rats
- PMID: 33620697
- PMCID: PMC8099953
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-021-00641-8
Paraventricular Nucleus P2X7 Receptors Aggravate Acute Myocardial Infarction Injury via ROS-Induced Vasopressin-V1b Activation in Rats
Abstract
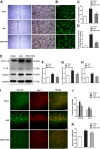
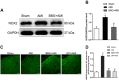
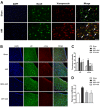
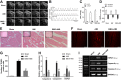
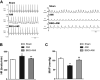
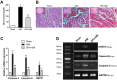
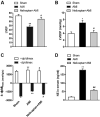
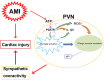
The present study was designed to investigate the mechanisms by which P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs) mediate the activation of vasopressinergic neurons thereby increasing sympathetic hyperactivity in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus of rats with acute myocardial ischemia (AMI). The left anterior descending branch of the coronary artery was ligated to induce AMI in rats. The rats were pretreated with BBG (brilliant blue G, a P2X7R antagonist), nelivaptan (a vasopressin V1b receptor antagonist), or diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) [an nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase inhibitor]. Hemodynamic parameters of the heart were monitored. Myocardial injury and cardiomyocyte apoptosis were assessed. In the PVN of AMI rats, P2X7R mediated microglial activation, while reactive oxygen species (ROS) and NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) were higher than in the sham group. Intraperitoneal injection of BBG effectively reduced ROS production and vasopressin expression in the PVN of AMI rats. Moreover, both BBG and DPI pretreatment effectively reduced sympathetic hyperactivity and ameliorated AMI injury, as represented by reduced inflammation and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. Furthermore, microinjection of nelivaptan into the PVN improved cardiac function and reduced the norepinephrine (AE) levels in AMI rats. Collectively, the results suggest that, within the PVN of AMI rats, P2X7R upregulation mediates microglial activation and the overproduction of ROS, which in turn activates vasopressinergic neuron-V1b receptors and sympathetic hyperactivity, hence aggravating myocardial injury in the AMI setting.
Keywords: Myocardial ischemia; P2X7 receptor; PVN; Reactive oxygen species; Vasopressin; c-fos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lin SK, Liu JM, Chang YH, Ting YT, Pang ST, Hsu RJ, et al. Increased risk of endotracheal intubation and heart failure following acute myocardial infarction in patients with urolithiasis: a nationwide population-based study. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:245–253. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S123702. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

