Quality of life in enuretic children
- PMID: 33620999
- PMCID: PMC7993947
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0308
Quality of life in enuretic children
Abstract
Introduction: Nocturnal enuresis is a highly incident chronic disorder that generates countless problems to the child and their parents. Bed-wetting has significant negative impacts on self-esteem and the performance of children. The aim of the current study is to assess the quality of life of enuretic children, as well as its association to sex and age.
Patients and methods: Thirty-nine enuretic children (23 boys) and 49 healthy children (27 boys) without any history of previous treatment for enuresis or voiding dysfunction were included. Age ranged between 6 and 11 years old. The "AUQEI" questionnaire was applied in a private environment to all children by the same researcher (psychologist) to evaluate quality of life.
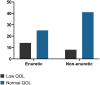
Results: Enuretic children displayed loss in quality of life when compared to non-enuretic (35.9% of enuretic x 16.3% of non-enuretic, p=0.035). They were mostly affected in their daily activities (p=0.02). No significant differences were found in the association of sex and gender with quality of life. These results suggest that, children with nocturnal enuresis have 2.87 times more chances of having loss in quality of life compared to non-enuretic.
Conclusions: Enuresis has a great impact in quality of life of children. This impact is not related to the age or sex of the child.
Keywords: Nocturnal Enuresis; Child; Quality of Life.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial Comment: Quality of life in enuretic children.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 May-Jun;47(3):542-543. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0308.1. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33621000 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- 1. Franco I, von Gontard A, De Gennaro M; International Childrens's Continence Society. Evaluation and treatment of nonmonosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a standardization document from the International Children's Continence Society. J Pediatr Urol. 2013; 9:234-43. - PubMed
-
- 2. Sarici H, Telli O, Ozgur BC, Demirbas A, Ozgur S, Karagoz MA. Prevalence of nocturnal enuresis and its influence on quality of life in school-aged children. J Pediatr Urol. 2016; 12:159.e1-159.e6. - PubMed
-
- 3. Savaser S, Kizilkaya Beji N, Aslan E, Gozen D. The Prevalence of Diurnal Urinary Incontinence and Enuresis and Quality of Life: Sample of School. Urol J. 2018;15:173-9. - PubMed
-
- 4. Kilicoglu AG, Mutlu C, Bahali MK, Adaletli H, Gunes H, Duman HM, et at. Impact of enuresis nocturna on health-related quality of life in children and their mothers. J Pediatr Urol. 2014; 10:1261-6. - PubMed
-
- 5. Meydan EA, Civilibal M, Elevli M, Duru NS, Civilibal N. The quality of life of mothers of children with monosymptomatic enuresis nocturna. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012; 44:655-9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical