Diagnosis for COVID-19: current status and future prospects
- PMID: 33621145
- PMCID: PMC7938658
- DOI: 10.1080/14737159.2021.1894930
Diagnosis for COVID-19: current status and future prospects
Abstract
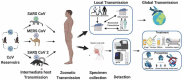
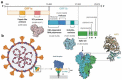
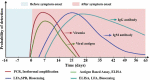
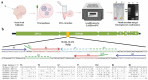
Introduction: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a respiratory illness caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), had its first detection in December 2019 in Wuhan (China) and spread across the world. In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic disease. The utilization of prompt and accurate molecular diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 virus, isolating the infected patients, and treating them are the keys to managing this unprecedented pandemic. International travel acted as a catalyst for the widespread transmission of the virus.Areas covered: This review discusses phenotype, structural, and molecular evolution of recognition elements and primers, its detection in the laboratory, and at point of care. Further, market analysis of commercial products and their performance are also evaluated, providing new ways to confront the ongoing global public health emergency.Expert commentary: The outbreak for COVID-19 created mammoth chaos in the healthcare sector, and still, day by day, new epicenters for the outbreak are being reported. Emphasis should be placed on developing more effective, rapid, and early diagnostic devices. The testing laboratories should invest more in clinically relevant multiplexed and scalable detection tools to fight against a pandemic like this where massive demand for testing exists.
Keywords: Biosensing; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis; point of care.
Figures





References
-
- Drosten C, Günther S, Preiser W, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(20):1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Zaki AM, Van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, et al. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(19):1814–1820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
