What do Transcription Factors Interact With?
- PMID: 33621520
- PMCID: PMC8184585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166883
What do Transcription Factors Interact With?
Abstract
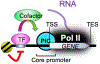
Although we have made significant progress, we still possess a limited understanding of how genomic and epigenomic information directs gene expression programs through sequence-specific transcription factors (TFs). Extensive research has settled on three general classes of TF targets in metazoans: promoter accessibility via chromatin regulation (e.g., SAGA), assembly of the general transcription factors on promoter DNA (e.g., TFIID), and recruitment of RNA polymerase (Pol) II (e.g., Mediator) to establish a transcription pre-initiation complex (PIC). Here we discuss TFs and their targets. We also place this in the context of our current work with Saccharomyces (yeast), where we find that promoters typically lack an architecture that supports TF function. Moreover, yeast promoters that support TF binding also display interactions with cofactors like SAGA and Mediator, but not TFIID. It is unknown to what extent all genes in metazoans require TFs and their cofactors.
Keywords: enhancers; gene regulation models; promoters; transcription mechanisms.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: BFP has a financial interest in Peconic, LLC, which uses the ChIP-exo technology implemented in this study and could potentially benefit from the outcomes of this research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A high-resolution protein architecture of the budding yeast genome.Nature. 2021 Apr;592(7853):309-314. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03314-8. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33692541 Free PMC article.
-
The general transcription machinery and general cofactors.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 May-Jun;41(3):105-78. doi: 10.1080/10409230600648736. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16858867 Review.
-
Regulation of the RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex by its associated coactivators.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Nov;24(11):767-782. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00630-9. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 37532915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A transcription factor IIA-binding site differentially regulates RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription in a promoter context-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 14;292(28):11873-11885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770412. Epub 2017 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28539359 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediator complex and transcription regulation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Nov-Dec;48(6):575-608. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.840259. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24088064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes in Gene Promoters and the First Introns Associated with Transcriptional Regulation in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 17;26(14):6874. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146874. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725120 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and Functions of the RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery during the Transcription Cycle.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 1;14(2):176. doi: 10.3390/biom14020176. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TFIID dependency of steady-state mRNA transcription altered epigenetically by simultaneous functional loss of Taf1 and Spt3 is Hsp104-dependent.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 9;18(2):e0281233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281233. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36757926 Free PMC article.
-
Different transcriptional responses by the CRISPRa system in distinct types of heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 9;12(1):11702. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15944-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35810197 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time visualization of reconstituted transcription reveals RNA polymerase II activation mechanisms at single promoters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 6:2025.01.06.631569. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.06.631569. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39829877 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

