Updated Japanese growth references for infants and preschool children, based on historical, ethnic and environmental characteristics
- PMID: 33622032
- PMCID: PMC4114539
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.12587
Updated Japanese growth references for infants and preschool children, based on historical, ethnic and environmental characteristics
Abstract
Aim: To provide updated growth references for Japanese children from birth to 6 years of age, for use in both growth monitoring and child care.
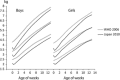
Methods: We analysed data from two national representative surveys that provided cross-sectional data on 3000 areas in the 2005 national census and longitudinal data from 136 hospitals. Growth references for length/height, weight, head circumference and chest circumference were constructed using the lambda-mu-sigma (LMS) method, with estimates of the L, M and S parameters. These updated values were then compared with growth references published by the World Health Organization.
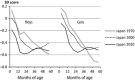
Results: The 3rd, 50th and 97th smoothed percentile values of length/height, weight, head circumference and chest circumference for boys and girls from birth to 6 years are presented. The comparisons show some large differences in median measurements between the charts.
Conclusion: Our growth references are based on a current, nationally representative sample of Japanese children. The results provide deep insight into child growth from a historical, ethnic and environmental point of view.
Keywords: Growth reference; Infants; LMS method; Neonatal weight loss; Preschool children.
©2014 The Authors. Acta Paediatrica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Foundation Acta Paediatrica.
Figures

References
-
- Cole TJ. Growth references and standards: In Cameron N, editor. “Human growth and development”. London: Academic, 2012: 537–66
-
- Yoshinaga S. Growth reference for infants in Japan. J Jpn Pediatr Soc 1929; 357: 325–36
-
- Saito K, Shimizu M. Physical growth of infants and preschool children in Japan. J Jpn Pediatr Soc 1949; 53: 1–6
-
- Kuriyama S, Saito K, Funakawa H. Physical growth of children in Japan (1950). J Jpn Pediatr Soc 1953; 57: 117–23
-
- Funakawa H, Hayashi M, Takaishi M. Physical growth of infants and preschool children in Japan (1960). J Child Health 1962; 21: 19–29
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

