Causes and timing of death in critically ill COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33622349
- PMCID: PMC7901794
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03492-x
Causes and timing of death in critically ill COVID-19 patients
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
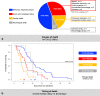
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

