Association between problematic social media use and memory performance in a sample of Lebanese adults: the mediating effect of anxiety, depression, stress and insomnia
- PMID: 33622360
- PMCID: PMC7901207
- DOI: 10.1186/s13005-021-00260-8
Association between problematic social media use and memory performance in a sample of Lebanese adults: the mediating effect of anxiety, depression, stress and insomnia
Abstract
Background: Psychological factors such as depression, anxiety, stress and insomnia and problematic social media use are able to alter our memories and might have an impact on memory function and retrieval. More studies are needed to better understand the relationship between memory performance and mental health disorders, especially the ones that could be related to problematic social media use. The objective of this study was to evaluate any association between problematic social media use, depression, anxiety, stress, and insomnia vs memory performance among a representative sample of Lebanese people.
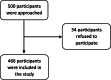
Methods: This cross-sectional study, conducted between January and May 2019, enrolled 466 community dwelling participants using a proportionate random sample from all Lebanese governorates. The questionnaire consisted of the following measures: the Memory Awareness Rating Scale (MARS) to assesses views of memory performance, the problematic social media use scale to measure the degree of addiction to social media, the Hamilton depression rating scale and Hamilton anxiety scale to assess depression and anxiety respectively, the Beirut Distress Scale to assess stress and the Lebanese Insomnia sale to assess insomnia. The data analysis was performed using the SPSS software version 25. A linear regression was conducted, taking the memory performance scale as the dependent variable. A mediation analysis was performed to test the effect of problematic social media use on memory performance mediated by depression, anxiety, stress and insomnia.
Results: Higher problematic social media use (Beta = - 0.21) and higher anxiety (Beta = - 0.25) were significantly associated with lower memory performance. The association between problematic social media use and memory performance was partially mediated by anxiety (21.19%) but not depression, stress or insomnia.
Conclusion: Concerning problematic social media use, a clear correlation was demonstrated in this study linking it to lower memory performances. Future studies should evaluate the possible mechanisms and methods for effective awareness especially towards the younger generation.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Insomnia; Memory performance; Problematic social media use; Stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

 —observed variable;
—observed variable;  —latent variable;
—latent variable;  —impact of one variable on another; e—residual error in the prediction of an unobserved factor; * p < 0.001. Numbers without a * indicate non-significant associations. The values of standardized coefficients are presented
—impact of one variable on another; e—residual error in the prediction of an unobserved factor; * p < 0.001. Numbers without a * indicate non-significant associations. The values of standardized coefficients are presentedSimilar articles
-
Problematic social media use and mental health (depression, anxiety, and insomnia) among Lebanese adults: Any mediating effect of stress?Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2021 Apr;57(2):539-549. doi: 10.1111/ppc.12576. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2021. PMID: 32633428
-
Association Between Problematic Social Media Use and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in a Sample of Lebanese Adults.Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2022 Feb 24;24(2):21m03025. doi: 10.4088/PCC.21m03025. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2022. PMID: 35213943
-
Prevalence and Factors Associated with Insomnia Among a Representative Sample of the Lebanese Population: Results of a Cross-Sectional Study.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2020 Jun;10(2):124-130. doi: 10.2991/jegh.k.200117.001. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32538027 Free PMC article.
-
Association between perceived stress and depression among medical students during the outbreak of COVID-19: The mediating role of insomnia.J Affect Disord. 2021 Sep 1;292:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.028. Epub 2021 May 27. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 34107425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of symptoms of depression, anxiety, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder, and psychological distress among populations affected by the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Psychiatry Res. 2021 Jan;295:113599. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113599. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Psychiatry Res. 2021. PMID: 33285346 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The relationship between loneliness and problematic social media usage in Chinese university students: a longitudinal study.BMC Psychol. 2024 Jan 4;12(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40359-023-01498-4. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38178215 Free PMC article.
-
Association between WeChat Use and Memory Performance among Older Adults in China: The Mediating Role of Depression.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;12(9):323. doi: 10.3390/bs12090323. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135127 Free PMC article.
-
Trait Anxiety and Social Media Fatigue: Fear of Missing Out as a Mediator.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2021 Sep 29;14:1499-1507. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S319379. eCollection 2021. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2021. PMID: 34616190 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Adolescents Regarding the Indirect Effect of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress between TikTok Use Disorder and Memory Loss.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 21;18(16):8820. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168820. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444569 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between technology addictions and schizotypal traits: mediating roles of depression, anxiety, and stress.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Jan 25;23(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04563-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36698079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shukal OP. Excellence in life: Gyan publishing house. 2007.
-
- Eysenck M. Attention and arousal: cognition and performance: Springer Science & Business Media. 2012.
-
- Eleven Factors that Influence Memory Process in Humans. Available from: http://www.psychologydiscussion.net/memory/11-factors-that-influence-mem...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

