The SimpliciT1 Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1b/2 Adaptive Study of TTP399, a Hepatoselective Glucokinase Activator, for Adjunctive Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 33622669
- PMCID: PMC7985421
- DOI: 10.2337/dc20-2684
The SimpliciT1 Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1b/2 Adaptive Study of TTP399, a Hepatoselective Glucokinase Activator, for Adjunctive Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Despite advances in exogenous insulin therapy, many patients with type 1 diabetes do not achieve acceptable glycemic control and remain at risk for ketosis and insulin-induced hypoglycemia. We conducted a randomized controlled trial to determine whether TTP399, a novel hepatoselective glucokinase activator, improved glycemic control in people with type 1 diabetes without increasing hypoglycemia or ketosis.
Research design and methods: SimpliciT1 was a phase 1b/2 adaptive study. Phase 2 activities were conducted in two parts. Part 1 randomly assigned 20 participants using continuous glucose monitors and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). Part 2 randomly assigned 85 participants receiving multiple daily injections of insulin or CSII. In both parts 1 and 2, participants were randomly assigned to 800 mg TTP399 or matched placebo (fully blinded) and treated for 12 weeks. The primary end point was change in HbA1c from baseline to week 12.
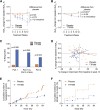
Results: The difference in change in HbA1c from baseline to week 12 between TTP399 and placebo was -0.7% (95% CI -1.3, -0.07) in part 1 and -0.21% (95% CI -0.39, -0.04) in part 2. Despite a greater decrease in HbA1c with TTP399, the frequency of severe or symptomatic hypoglycemia decreased by 40% relative to placebo in part 2. In both parts 1 and 2, plasma β-hydroxybutyrate and urinary ketones were lower during treatment with TTP399 than placebo.
Conclusions: TTP399 lowers HbA1c and reduces hypoglycemia without increasing the risk of ketosis and should be further evaluated as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of type 1 diabetes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03335371.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . 6. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43(Suppl. 1):S66–S76 - PubMed
-
- Froguel P, Vaxillaire M, Sun F, et al. . Close linkage of glucokinase locus on chromosome 7p to early-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 1992;356:162–164 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

