Systematic functional analysis of Leishmania protein kinases identifies regulators of differentiation or survival
- PMID: 33623024
- PMCID: PMC7902614
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21360-8
Systematic functional analysis of Leishmania protein kinases identifies regulators of differentiation or survival
Abstract
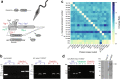
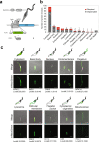
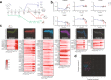
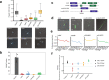
Differentiation between distinct stages is fundamental for the life cycle of intracellular protozoan parasites and for transmission between hosts, requiring stringent spatial and temporal regulation. Here, we apply kinome-wide gene deletion and gene tagging in Leishmania mexicana promastigotes to define protein kinases with life cycle transition roles. Whilst 162 are dispensable, 44 protein kinase genes are refractory to deletion in promastigotes and are likely core genes required for parasite replication. Phenotyping of pooled gene deletion mutants using bar-seq and projection pursuit clustering reveal functional phenotypic groups of protein kinases involved in differentiation from metacyclic promastigote to amastigote, growth and survival in macrophages and mice, colonisation of the sand fly and motility. This unbiased interrogation of protein kinase function in Leishmania allows targeted investigation of organelle-associated signalling pathways required for successful intracellular parasitism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Raising the Bar(-seq) in Leishmania Genetic Screens.Trends Parasitol. 2021 May;37(5):367-369. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.03.002. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Trends Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33773911
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

