Biosensors promising bio-device for pandemic screening "COVID-19"
- PMID: 33623173
- PMCID: PMC7892310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.microc.2021.106094
Biosensors promising bio-device for pandemic screening "COVID-19"
Abstract
Undoubtedly, the coronavirus pandemic is one of the most influential events not only in medicine but also in the economic field in the world. Rapid transmission and high mortality rates, as well as prolonged and asymptomatic communal periods, are the most important reasons for the global panic due to coronavirus. Since coronavirus treatment and specific vaccines are not yet available, early detection of the virus is critical. A rapid and accurate diagnosis can play a crucial role in the treatment and control of the COVID 19 disease. Serological, ELISA, and molecular-based tests, including PCR and RT-PCR, are among the most important routine methods for detecting coronaviruses. False-positive/negative results, low sensitivity and specificity, and the need for advanced equipment are among the disadvantages and problems of routine methods. To eliminate the drawbacks of routine methods, new technologies are being developed. Biosensors are one of the most important ones. This paper is a summary of the up-to-date states of innovative bio-sensing tools for the ultrasensitive detection of coronaviruses (COVID 19) with encouraging uses for future challenges in disease diagnosis.
Keywords: Biosensors; Conventional methods; Coronaviruses (COVID 19); Pandemic.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


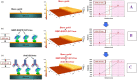
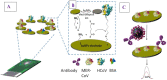
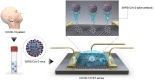
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review on current COVID-19 detection methods: From lab care to point of care diagnosis.Sens Int. 2021;2:100119. doi: 10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100119. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Sens Int. 2021. PMID: 34766062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laboratory-Based Resources for COVID-19 Diagnostics: Traditional Tools and Novel Technologies. A Perspective of Personalized Medicine.J Pers Med. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):42. doi: 10.3390/jpm11010042. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33451039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Applications of separation technology in novel coronavirus research, epidemic prevention and detection].Se Pu. 2021 Jul 8;39(7):679-685. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.03022. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227364 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
[Evaluation of the Rapid Antigen Detection Kit with the Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Respiratory Samples].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022 Apr;56(2):263-273. doi: 10.5578/mb.20229806. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022. PMID: 35477229 Turkish.
-
A review on corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): current progress, clinical features and bioanalytical diagnostic methods.Mikrochim Acta. 2022 Feb 14;189(3):103. doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05167-y. Mikrochim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35157153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Methods in biosensors and biomolecular electronics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 17;11:1294221. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1294221. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37915550 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Integrating bio medical sensors in detecting hidden signatures of COVID-19 with Artificial intelligence.Measurement (Lond). 2022 May 15;194:111054. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111054. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Measurement (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35368881 Free PMC article.
-
Current state of diagnostic, screening and surveillance testing methods for COVID-19 from an analytical chemistry point of view.Microchem J. 2021 Aug;167:106305. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2021.106305. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Microchem J. 2021. PMID: 33897053 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Biosensors' Scientific Production and Research Patterns: A Bibliometric Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 12;24(10):3082. doi: 10.3390/s24103082. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilizing Electrochemical-Based Sensing Approaches for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;12(7):473. doi: 10.3390/bios12070473. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Corman V., Eckerle I., Bleicker T., Zaki A., Landt O., Eschbach-Bludau M., van Boheemen S., Gopal R., Ballhause M., Bestebroer T. Detection of a novel human coronavirus by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Eurosurveillance. 2012;17(39) - PubMed
-
- Ralph R., Lew J., Zeng T., Francis M., Xue B., Roux M., Ostadgavahi A.T., Rubino S., Dawe N.J., Al-Ahdal M.N. 2019-nCoV (Wuhan virus), a novel Coronavirus: human-to-human transmission, travel-related cases, and vaccine readiness. J. Infect. Dev. Countr. 2020;14(01):3–17. - PubMed
-
- Shirato K., Semba S., El-Kafrawy S.A., Hassan A.M., Tolah A.M., Takayama I., Kageyama T., Notomi T., Kamitani W., Matsuyama S. Development of fluorescent reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) using quenching probes for the detection of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. Methods. 2018;258:41–48. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
