To Compare the Efficacy of Two Intravenous Combinations of Drugs Ketamine-Propofol vs Ketamine-Dexmedetomidine for Sedation in Children Undergoing Dental Treatment
- PMID: 33623343
- PMCID: PMC7887178
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1826
To Compare the Efficacy of Two Intravenous Combinations of Drugs Ketamine-Propofol vs Ketamine-Dexmedetomidine for Sedation in Children Undergoing Dental Treatment
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy of two intravenous combinations of drugs ketamine-propofol (KP) vs ketamine-dexmedetomidine (KD) for sedation in children undergoing dental treatment.
Study design: Thirty patients were selected, evaluated according to the predetermined criteria and divided in equal numbers of 15 amongst 2 groups KP and KD.
Materials and methods: Informed consent was taken, nil per oral (NPO) guidelines were followed and the study drug was administered. Dental procedure was performed. Heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP) and oxygen saturation (SPO2) were monitored continuously throughout the procedure. The modified Ramsay sedation (MRS) score was recorded along with Houpt sedation score. Recovery status was accessed by modified Aldrete's recovery scale.
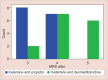
Statistical analysis: Student t test was used for comparing HR, BP and SPO2. Chi-square test was used to compare MRS, Houpt sedation score and modified Aldrete's recovery scale amongst the two groups KP and KD.
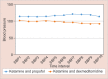
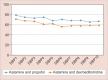
Results: The sedation achieved with both the groups was adequate. Both the drugs produce adequate hemodynamic stability.
Conclusion: Ketamine-dexmedetomidine has a better efficacy over the other group, ketamine-propofol.
How to cite this article: Joshi AB, Shankaranarayan UR, Hegde A, et al. To Compare the Efficacy of Two Intravenous Combinations of Drugs Ketamine-Propofol vs Ketamine-Dexmedetomidine for Sedation in Children Undergoing Dental Treatment. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2020;13(5):529-535.
Keywords: Dental treatment; Dexmedetomidine; Intravenous sedation; Ketamine; Propofol.
Copyright © 2020; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ketamine and dexmedetomidine (Keto-dex) or ketamine and propofol (Keto-fol) for procedural sedation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: Which is safer? A randomized clinical trial.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec;41(6):583-590. doi: 10.1007/s12664-022-01291-y. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36576697 Clinical Trial.
-
Ketamine-propofol vs ketamine-dexmedetomidine combinations in pediatric patients undergoing burn dressing changes.J Burn Care Res. 2012 Nov-Dec;33(6):718-22. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3182504316. J Burn Care Res. 2012. PMID: 22878491 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of ketamine-dexmedetomidine versus ketamine-propofol combinations for sedation in patients after coronary artery bypass graft surgery.Ann Card Anaesth. 2017 Apr-Jun;20(2):182-187. doi: 10.4103/aca.ACA_254_16. Ann Card Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 28393778 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol/dexmedetomidine and propofol/ketamine combinations for anesthesia in pediatric patients undergoing transcatheter atrial septal defect closure: a prospective randomized study.Clin Ther. 2010 Apr;32(4):701-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.010. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20435239 Clinical Trial.
-
Conscious Sedation: Emerging Trends in Pediatric Dentistry.Anesth Essays Res. 2017 Apr-Jun;11(2):277-281. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.171458. Anesth Essays Res. 2017. PMID: 28663606 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of intravenous sedation with propofol, dexmedetomidine and midazolam in double-J ureteral stent removal.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023 Apr 15;11(2):160-167. eCollection 2023. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023. PMID: 37168936 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Ketamine-Dexmedetomidine Versus Ketamine-Propofol Combination for Periprocedural Sedation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 Apr;28(4):211-227. doi: 10.1007/s11916-023-01208-0. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38214834 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine and propofol in reducing recovery agitation in pediatric patients after ketamine procedural sedation in emergency department.J Res Med Sci. 2021 Aug 30;26:61. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_661_20. eCollection 2021. J Res Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34729069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roelofse JA, Joubert JJ, Roelofse PG. A double-blind randomized comparison of midazolam alone and midazolam combined with ketamine for sedation of pediatric dental patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;54(7):838–844. - PubMed
-
- Tickle M, Milsom K, King D, et al. The fate of the carious primary teeth of children who regularly attend the general dental service. Br Dent J. 2002;192(4):219–223. - PubMed
-
- Alfonzo-Echeverri EC, Berg JH, Wild TW, et al. Oral ketamine for pediatric outpatient dental surgery sedation. Pediatr Dent. 1993;15(3):182–185. - PubMed
-
- Sekerci C, Dönmez A, Ateş Y, et al. Oral ketamine premedication in children (placebo controlled double-blind study). Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1997;13(6):606–611. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources