AG-1024 Sensitizes Sorafenib-Resistant Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib via Enhancing G1/S Arrest
- PMID: 33623392
- PMCID: PMC7894871
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S289324
AG-1024 Sensitizes Sorafenib-Resistant Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib via Enhancing G1/S Arrest
Abstract
Purpose: The frequency in resistance to sorafenib accounts for the grim prognosis of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In the present study, we explore the anti-cancer efficacy of co-administration of sub-toxic AG-1024 with sorafenib in HCC cells to enhance the sensitivity of these cells to sorafenib.
Materials and methods: Two acquired sorafenib-resistant HCC cells, SNU-sora-5 and SK-sora-5, were established and verified. The MTT assay, colony formation assay, cell morphology detection and flow cytometric analysis were then used to determine the anti-tumor effects of the co-administration of sub-toxic AG-1024 and sorafenib. Finally, the potential molecular mechanism was preliminarily examined.
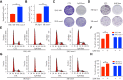
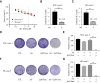
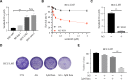
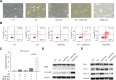
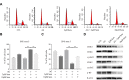
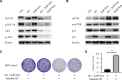
Results: Compared to parental cell lines, the acquired sorafenib-resistant cell lines, SNU-sora-5 and SK-sora-5, were more resistant to sorafenib. Sub-toxic AG-1024 markedly enhanced sorafenib-mediated cell inhibition in acquired sorafenib-resistant HCC strains, with a reversal index (RI) of 4.64 in SNU-sora-5 and 4.58 in SK-sora-5 cell lines. Moreover, co-administration of sub-toxic AG-1024 and sorafenib exerted dramatic cytotoxicity compared with sorafenib alone in the intrinsic sorafenib-resistant HCC-LM3 cells. In contrast to high-dose sorafenib, sub-toxic AG-1024 combined with sorafenib had less impact on apoptosis while significantly enhancing G1/S arrest via activation of the mTOR/p21 signaling pathway. The more, pharmacological inhibition of mTOR activity by inhibitor Palomid 529 significantly antagonized the synergistic anti-cancer effects of AG-1024 and sorafenib in HCC cells.
Conclusion: The current findings indicate that sub-toxic AG-1024 may be a promising therapeutic agent in enhancing the sensitivity in HCC cells to sorafenib, bringing hope to HCC patients refractory to sorafenib treatment.
Keywords: AG-1024; G1/S arrest; hepatocellular carcinoma; mTOR; sorafenib resistance.
© 2021 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simvastatin re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by inhibiting HIF-1α/PPAR-γ/PKM2-mediated glycolysis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jan 30;39(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-1528-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32000827 Free PMC article.
-
Pristimerin synergistically sensitizes conditionally reprogrammed patient derived-primary hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib through endoplasmic reticulum stress and ROS generation by modulating Akt/FoxO1/p27kip1 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jun;86:153563. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153563. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33951569
-
Cabazitaxel, a novel chemotherapeutic alternative for drug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Jul 1;8(7):1297-1306. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30094102 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking effects of mTOR, PI3K, and dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors in hepatocellular and renal cell carcinoma models developing resistance to sunitinib and sorafenib.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 May;71(5):1297-307. doi: 10.1007/s00280-013-2129-6. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23479136
-
HANR Enhances Autophagy-Associated Sorafenib Resistance Through miR-29b/ATG9A Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Mar 9;13:2127-2137. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S229913. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32210579 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Sorafenib-Ruthenium Complexes, Investigation of Biological Activities and Applications in Drug Delivery Systems as an Anticancer Agent.J Med Chem. 2024 Mar 28;67(6):4463-4482. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01115. Epub 2024 Mar 12. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38471014 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning model reveals roles of interferon‑stimulated genes in sorafenib‑resistant liver cancer.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 15;28(3):438. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14571. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39081963 Free PMC article.
-
New Opportunities in the Systemic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Today and Tomorrow.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1456. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031456. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morse DC, Chockalingam R, Pye A, Huen A. Hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sorafenib initiation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:AB219–AB219. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

