Transiently Elevated TC and sdLDL-C Levels and Falsely Low LDL-C Levels in Patients with Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 33623393
- PMCID: PMC7894891
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S285856
Transiently Elevated TC and sdLDL-C Levels and Falsely Low LDL-C Levels in Patients with Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Most patients diagnosed with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ECCA) exhibit cholestasis caused by obstruction of the bile duct. Cholestasis is associated with lipid disorders, but studies focused on the changing lipid parameters in patients with ECCA are lacking. Here, we observed lipid profiles in patients with ECCA and investigated whether the removal of biliary obstruction could correct dyslipidemia.
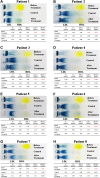
Patients and methods: We consecutively included patients admitted to the hepatobiliary surgery department at the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University. The patients were divided into an ECCA group or a non-ECCA group based on the disease assessment. Patients with histological confirmation of ECCA were included in the ECCA group. Blood samples were collected on admission as well as five days after treatment. An automatic biochemistry analyzer was used to test liver function and serum lipid levels. Serum lipoprotein electrophoresis was performed using barbitone sodium buffer and Sudan black B.
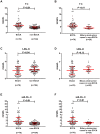
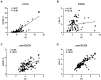
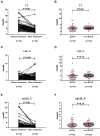
Results: A total of 180 patients met inclusion criteria and were enrolled for this study. Of these, 76 patients were diagnosed with ECCA; all other patients were enrolled in the non-ECCA group. Total cholesterol (TC) and small and dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (sdLDL-C) levels were significantly elevated in the ECCA group. LDL-C levels were found to be slightly lower in the ECCA group. In the ECCA group, serum samples were detained in sample wells and lipoproteins failed to be separated. TC and sdLDL-C levels significantly decreased after cholestasis relief in the ECCA group. Lipoprotein electrophoresis revealed that patients with ECCA showed normal lipoprotein patterns after treatment.
Conclusion: Patients with ECCA exhibited transiently elevated TC and sdLDL-C levels and falsely low LDL-C results. TC, sdLDL-C, and LDL-C levels could be restored to normal levels after biliary obstruction removal and cholestasis relief.
Keywords: LDL-C; TC; cholestasis; dyslipidemia; extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; sdLDL-C.
© 2021 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small Dense Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, Paraoxonase 1 and Lipid Profile in Postmenopausal Women: Quality or Quantity?Arch Med Res. 2015 Oct;46(7):534-8. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Sep 5. Arch Med Res. 2015. PMID: 26348135
-
Association between high-normal levels of alanine aminotransferase and risk factors for atherogenesis.Gastroenterology. 2013 Dec;145(6):1271-9.e1-3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.036. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23973920 Free PMC article.
-
Association between carotid intima media thickness and small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in acute ischaemic stroke.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jul 28;19(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01353-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32723324 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hepatol. 2020 Jan;72(1):95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31536748
-
Small dense low-density lipoprotein-lowering agents.Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 25;401(10):1101-1121. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2019-0426. Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32427116 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Implications of Naples Prognostic Score for Patients with Resected Cholangiocarcinoma: A Real-World Experience.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Feb 2;17:655-667. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S446735. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38328562 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

