An Overview of Current Uses and Future Opportunities for Computer-Assisted Design of Vaccines for Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PMID: 33623396
- PMCID: PMC7894434
- DOI: 10.2147/AABC.S258759
An Overview of Current Uses and Future Opportunities for Computer-Assisted Design of Vaccines for Neglected Tropical Diseases
Abstract
Neglected tropical diseases are infectious diseases that impose high morbidity and mortality rates over 1.5 billion people worldwide. Originally restricted to tropical and subtropical regions, changing climate conditions have increased their potential to emerge elsewhere. Control of their impact suffers from shortages like poor epidemiological surveillance or irregular drug distribution, and some NTDs still lack of appropriate diagnostics and/or efficient therapeutics. For these, availability of vaccines to prevent new infections, or the worsening of those already established, would mean a major breakthrough. However, only dengue and rabies count with approved vaccines at present. Herein, we review the state-of-the-art of vaccination strategies for NTDs, setting the focus on third generation vaccines and the concept of reverse vaccinology. Its capability to address pathogens´ biological complexity, likely contributing to save developmental costs is discussed. The use of computational tools is a fundamental aid to analyze increasingly large datasets aimed at designing vaccine candidates with the highest, possibly, opportunities to succeed. Ultimately, we identify and analyze those studies that took an in silico approach to find vaccine candidates, and experimentally assessed their immunogenicity and/or protection capabilities.
Keywords: epitopes; immunoinformatics; neglected tropical diseases; reverse vaccinology; vaccines.
© 2021 Robleda-Castillo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
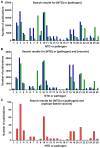
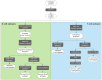
Similar articles
-
Developing plant-based vaccines against neglected tropical diseases: where are we?Vaccine. 2012 Dec 17;31(1):40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.10.094. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 23142588 Review.
-
Vaccines against Emerging and Neglected Infectious Diseases: An Overview.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;10(9):1385. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10091385. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36146463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time for T? Immunoinformatics addresses vaccine design for neglected tropical and emerging infectious diseases.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015 Jan;14(1):21-35. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.955478. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 25193104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New vaccines for neglected parasitic diseases and dengue.Transl Res. 2013 Sep;162(3):144-55. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.006. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23578479 Review.
-
Current progress of immunoinformatics approach harnessed for cellular- and antibody-dependent vaccine design.Pathog Glob Health. 2018 May;112(3):123-131. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2018.1446773. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Pathog Glob Health. 2018. PMID: 29528265 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
"Immunoinformatic Identification of T-Cell and B-Cell Epitopes From Giardia lamblia Immunogenic Proteins as Candidates to Develop Peptide-Based Vaccines Against Giardiasis".Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 27;11:769446. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.769446. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34778111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/diseases/en/. Accessed October7, 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

