Unintended Pregnancy and Associated Factors Among HIV Positive Women in Ilu Aba Bora zone, South Western Ethiopia: A Facility-Based Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 33623441
- PMCID: PMC7896757
- DOI: 10.2147/HIV.S288373
Unintended Pregnancy and Associated Factors Among HIV Positive Women in Ilu Aba Bora zone, South Western Ethiopia: A Facility-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Unintended pregnancy reflects the existence of unprotected sex. Understanding factors associated with unintended pregnancy among HIV-positive women is very important to design strategies for the prevention of further transmission and infection with the virus. However, there is scarce information in this regard. Given the degree of HIV prevalence among women and the current antiretroviral therapy scale up in Ethiopia, it is important to understand factors associated with un-intended pregnancy in order to prevent mother to child HIV transmission (MTCT).
Methods: An institution-based cross-sectional study design was employed. The sample size was 353; all HIV/AIDS sero-positive reproductive age group (15-49) women having any pregnancy history after their diagnosis and having started HAART were included and simple random sampling was used to select study participants. Data collection period was from March 9 to April 13, 2019.
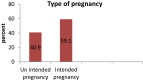
Results: The prevalence of unintended pregnancy among the participants was 40.9%. In the multivariate logistic regression, unemployment (AOR, 3.36; 95% CI: 1.55-7.26), not being knowledgeable on MTCT and prevention of MTCT (PMTCT) (AOR, 3.18; 95% CI: 1.92-5.24), and having had no discussion on reproductive health issues (AOR, 1.83; 95% CI: 1.09-3.07) are factors significantly associated with unintended pregnancy occurrence among HIV-positive women on antiretroviral therapy.
Conclusion and recommendation: The prevalence of unintended pregnancy among the women in the study is high. To avoid unintended pregnancies, HIV-infected women need access to effective family planning services and risk reduction discussions during routine care visits.
Keywords: Ilu Aba Bora zone; Southwest Ethiopia; unintended pregnancy; women on ART.
© 2021 Teklu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unintended Pregnancy and Associated Factors among Women Who Live in Ilu Gelan District, Western Ethiopia, 2021.Int J Reprod Med. 2022 Jan 21;2022:8646724. doi: 10.1155/2022/8646724. eCollection 2022. Int J Reprod Med. 2022. PMID: 35097105 Free PMC article.
-
Unmet need for family planning and factors associated among women living with HIV in Oromia regional state, Ethiopia.Reprod Health. 2021 Nov 13;18(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01280-y. Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 34774065 Free PMC article.
-
Awareness and knowledge on timing of mother-to-child transmission of HIV among antenatal care attending women in Southern Ethiopia: a cross sectional study.Reprod Health. 2013 Dec 13;10:66. doi: 10.1186/1742-4755-10-66. Reprod Health. 2013. PMID: 24330487 Free PMC article.
-
Demand for long acting contraceptive methods among married HIV positive women attending care at public health facilities at Bahir Dar City, Northwest Ethiopia.Reprod Health. 2015 Aug 27;12:76. doi: 10.1186/s12978-015-0073-0. Reprod Health. 2015. PMID: 26311141 Free PMC article.
-
HIV test coverage among pregnant women in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Afr J AIDS Res. 2021 Dec;20(4):259-269. doi: 10.2989/16085906.2021.1980066. Afr J AIDS Res. 2021. PMID: 34905450
Cited by
-
Using the Family Planning Estimation Tool (FPET) to assess national-level family planning trends and future projections for contraceptive prevalence and associated demand for HIV-infected women in sub-Saharan Africa.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Aug 6;4(8):e0002637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002637. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39106280 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of family planning into HIV services: a systematic review.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):393-403. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.2020893. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35098814 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of modern contraception and determinants among HIV positive women in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Nov 20;24(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03454-9. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39567937 Free PMC article.
-
Unintended pregnancy among women living with HIV and its predictors in East Africa, 2024. A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 27;19(12):e0310212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310212. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39729439 Free PMC article.
-
Correlates of unintended pregnancies among HIV+ women.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 Jun;14(6):2374-2379. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1884_24. Epub 2025 Jun 30. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40726690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS terminology guidelines (October 2011). 2011:16–23.
-
- Darak S, Hutter I, Kulkarni S, Kulkarni V, Janssen F. Occurrence of pregnancies among HIV infected Indian women: does knowledge about HIV status make a difference? Int J Popul Res. 2015;2015. doi:10.1155/2015/617907 - DOI
-
- Carolina N. 2007 STD incidence rates. 2007:129–154.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous