Rest/stress intradermal lymphoscintigraphy in diagnosis of lipedema
- PMID: 33623507
- PMCID: PMC7875021
- DOI: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_5_20
Rest/stress intradermal lymphoscintigraphy in diagnosis of lipedema
Abstract
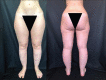
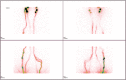
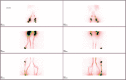
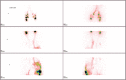
Lipedema is a chronic and progressive disease characterized by a symmetrical and bilateral swelling of the lower extremities. In general, the feet are not involved. Lipedema is believed to affect nearly 1 in 9 adult women worldwide. Despite this relatively common disease, lipedema is often confused with primary lymphedema or obesity. In clinically advanced lipedema stages, fat continues to build up and may block the lymphatic vessels causing a secondary lymphedema (Lipo-Lymphedema). We consecutively evaluated 54 women with a clinical diagnosis of lower limbs lipedema. Two doses of 99mTc-nanocolloid were injected intradermally at the first intermetatarsal space and in the lateral malleolar area. Two static planar scans were taken at rest immediately following the intradermal injection. Subsequently, all patients were asked to perform an isotonic muscular exercise (stepping) for 2 min. Then, post exercise scans were performed to monitor the tracer pathway. Subsequently, the patient was asked to take a 30-40 min walk (prolonged exercise) and delayed scans were acquired. In early clinical stages, the lymphatic flow is usually preserved and the rest/stress intradermal lymphoscintigraphy may visualize a normal lymphatic drainage with a frequent pattern (tortuous course) of the leg lymphatic pathway. In clinically advanced stages, lymph stagnation areas were observed. Unlike obesity, lipedema fat storage is resistant to dietary regimen, bariatric surgery, and physical activity. Surgical treatment (tumescent liposuction and reductive surgery) is the most effective treatment to remove adipose tissue. Complex decongestive therapies are helpful in reducing the lymph stagnation, especially in patients with advanced lipolymphedema.
Keywords: 99mTc-HSA; intradermal; lipedema; lymphoscintigraphy; stress.
Copyright: © 2020 World Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intradermal lymphoscintigraphy at rest and after exercise: a new technique for the functional assessment of the lymphatic system in patients with lymphoedema.Nucl Med Commun. 2010 Jun;31(6):547-51. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e328338277d. Nucl Med Commun. 2010. PMID: 20215978
-
Liposuction for the Treatment of Lipedema: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Jun 7. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Jun 7. PMID: 31479212 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Rest/Stress Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy for the Functional Imaging of the Lymphatic System.Clin Nucl Med. 2022 Dec 1;47(12):1011-1018. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000004422. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Clin Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 36183418
-
[Comparative analysis of lymphoscintigraphy between lipedema and lower limb lymphedema].J Mal Vasc. 2004 Dec;29(5):257-61. doi: 10.1016/s0398-0499(04)96770-4. J Mal Vasc. 2004. PMID: 15738837 French.
-
[Lipedema: a misdiagnosed entity].J Mal Vasc. 2012 Jul;37(4):213-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmv.2012.05.002. Epub 2012 Jun 13. J Mal Vasc. 2012. PMID: 22698628 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Brazilian Consensus Statement on Lipedema using the Delphi methodology.J Vasc Bras. 2025 Feb 10;24:e20230183. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.202301832. eCollection 2025. J Vasc Bras. 2025. PMID: 39949954 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Applications of Ketogenic Diets in Lipedema: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence.Curr Obes Rep. 2025 May 26;14(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s13679-025-00642-y. Curr Obes Rep. 2025. PMID: 40419722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic function and anatomy in early stages of lipedema.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022 Jul;30(7):1391-1400. doi: 10.1002/oby.23458. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022. PMID: 35707862 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphoscintigraphic alterations in lower limbs in women with lipedema in comparison to women with overweight/obesity.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 10;14:1099555. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1099555. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37101701 Free PMC article.
-
Functioning of People with Lipoedema According to All Domains of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 21;20(3):1989. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031989. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen EV, Hines EA. Lipedema of the legs: A syndrome characterized by fat legs and orthostatic edema. Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1940;15:184–7.
-
- Child AH, Gordon KD, Sharpe P, Brice G, Ostergaard P, Jeffery S, et al. Lipedema: An inherited condition. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:970–6. - PubMed
-
- Földi E, Földi M, Tischendorf F. Adipositas, lipedema and lymphostasis. Med Welt. 1983;34:198–200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

