A Network Pharmacology Approach to Explore the Mechanisms of Artemisiae scopariae Herba for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 33623529
- PMCID: PMC7875618
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6614039
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Explore the Mechanisms of Artemisiae scopariae Herba for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: As a traditional Chinese medicine, Artemisiae scopariae Herba (ASH) is used to treat various liver diseases. The purpose of this study was to explore the mechanisms of ASH for treating chronic hepatitis B (CHB) using a network pharmacological method.
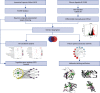
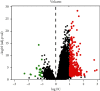
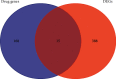
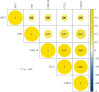
Methods: Bioactive ingredients and related targets of ASH were obtained from Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP) database. Gene names of targets were extracted from UniProt database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of CHB were obtained from microarray dataset GSE83148. The intersect genes between DEGs and target genes were annotated using clusterProfiler package. The STRING database was used to obtain a network of protein-protein interactions. Cytoscape 3.7.2 was used to construct the "ingredient-gene-pathway" (IGP) network. Molecular docking studies were performed using Autodock vina.
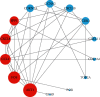
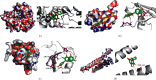
Results: A total of 13 active components were extracted from TCMSP database. Fifteen intersect genes were obtained between 183 target genes and 403 DEGs of GSE83148. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis results showed that ASH against CHB mainly involved in toll-like receptor signaling pathway, cellular senescence, hepatitis B, and chemokine signaling pathway. We screened one hub compound, five core targets, and four key pathways from constructed networks. The docking results indicated the strong binding activity between quercetin and AKT1.
Conclusions: This study provides potential molecular mechanisms of ASH against CHB based on exploration of network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2021 Asi He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of "Hedyotis Diffusae Herba-Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma" in treatment of lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Dec;46(23):6261-6270. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210913.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34951253 Chinese.
-
Analysis of the key prognostic genes and potential traditional Chinese medicine therapeutic targets in glioblastoma based on bioinformatics and network pharmacology methods.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 May;11(5):1386-1405. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-1122. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35706800 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the mechanism of colorectal cancer treatment using Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 14;16(6):e0252508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252508. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34125845 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Recent progress in the study of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba (Yin Chen), a promising medicinal herb for liver diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;130:110513. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110513. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32702631 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitigation of Gastric Damage Using Cinnamomum cassia Extract: Network Pharmacological Analysis of Active Compounds and Protection Effects in Rats.Plants (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;11(6):716. doi: 10.3390/plants11060716. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336597 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Investigate the Molecular Targets of Rhubarb for Treating Cancer.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 8;2021:9945633. doi: 10.1155/2021/9945633. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34211578 Free PMC article.
-
Through network pharmacology and molecular docking to explore the underlying mechanism of Artemisia annua L. treating in abdominal aortic aneurysm.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1034014. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1034014. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36338468 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: The mechanisms of signal pathway regulation.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 12;10(20):e39176. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39176. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39640799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of the Active Components and Mechanism of Forsythia suspensa Leaf against Respiratory Syncytial Virus Based on Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 20;2022:5643345. doi: 10.1155/2022/5643345. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35911158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y. P., Qiu X. Y., Liu Y., et al. Research progress on pharmacological effect of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 2019;50:2235–2241.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

