Case report: incidental findings of COVID-19 infection on positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging of a giant gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- PMID: 33623553
- PMCID: PMC7875735
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.supp.2020.35.2.23167
Case report: incidental findings of COVID-19 infection on positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging of a giant gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Abstract
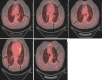
We report the incidental finding of COVID-19 in a 59-year-old male, with no significant cardiorespiratory past medical history who underwent a fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan for investigation of a likely gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). There may be significant discrepancies between clinical symptoms and radiological severity with COVID-19 infection. FDG-PET scanning has the potential to complement traditional radiological imaging in COVID-19 in diagnosis of subclinical diagnosis or early stage disease, as well as monitoring disease progression.
Keywords: Covid-19; FDG-PET; GIST; gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
©Hamish Reed-Embleton et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Prostate: Staging and Evaluation of Response to Therapy With 18F-FDG PET/CT.Clin Nucl Med. 2018 Jan;43(1):52-54. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000001906. Clin Nucl Med. 2018. PMID: 29166334
-
[The value of (18)F-FDG PET-CT imaging in predicting the malignant potential of GIST].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 23;39(11):821-827. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.11.004. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29151288 Chinese.
-
Gastric GIST Incidentally Detected on 68Ga-PSMA-PET/CT: Correlation Between Functional Imaging and Histology.Clin Nucl Med. 2018 Dec;43(12):e488-e491. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000002347. Clin Nucl Med. 2018. PMID: 30358621
-
Performance of F-18 FDG PET/CT for predicting malignant potential of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Mar;33(3):576-582. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14015. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 28994187
-
Role of ¹⁸F 2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography in upper gastrointestinal malignancies.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Dec 14;17(46):5059-74. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i46.5059. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22171140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Molecular Imaging: A Systematic Review of Incidental Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia on PET Studies.Semin Nucl Med. 2021 Mar;51(2):178-191. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Semin Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 33509374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center New Cases of COVID-19 In World Countries. 2020. Accessed Apr 24 2020.
-
- Zhou S, Wang Y, Zhu T, Xia L. Am J Roentgenol. Wuhan, China: 2020. CT features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in 62 patients in; pp. 1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous