Oncogenic mechanisms in renal insufficiency
- PMID: 33623673
- PMCID: PMC7886561
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa122
Oncogenic mechanisms in renal insufficiency
Abstract
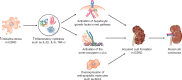
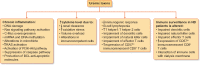
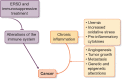
The prevalence of both cancer and end-stage renal disease is increasing. In addition, medical advances have meant increased survival rates for both diseases. Many chemotherapeutics are renally excreted, and conversely, renal insufficiency promotes a pro-neoplastic state, including genitourinary and other cancers. Dialysis prolongs life while increasing cancer risk. Proposed oncogenic mechanisms include immune dysfunction, chronic inflammation, changes in gut microbiota and stimulation of the renin-angiotensin system. This review summarizes current concepts in the relationship between cancer and renal insufficiency.
Keywords: cancer; carcinogenesis; end-stage renal disease; malignancy; renal transplant.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Maisonneuve P, Agodoa L, Gellert R. et al. Cancer in patients on dialysis for end-stage renal disease: an international collaborative study. Lancet 1999; 354: 93–99 - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Argani P, Tickoo S. et al. Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma (ACKD-RCC)-like cysts. Am J Surg Pathol 2018; 42: 1396–1401 - PubMed
-
- Oya M, Mikami S, Mizuno R. et al. c-Jun activation in acquired cystic kidney disease and renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 2005; 174: 726–730 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

