Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Circular RNA circ-ITCH Expression in Cancer Patients: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 33623789
- PMCID: PMC7875623
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8828299
Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Circular RNA circ-ITCH Expression in Cancer Patients: A Meta-analysis
Abstract
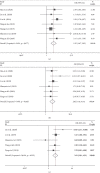
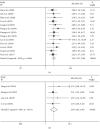
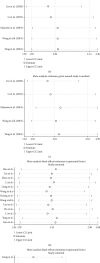
Circular RNAs are a class of RNAs with a covalently closed configuration, and several members of them have been reported to be capable of regulating various biological processes and predicting the outcome of disease. Among them, circular RNA circ-ITCH has been identified to be aberrantly expressed and associated with disease progression in diverse cancers. However, the correlation of circ-ITCH expression with clinicopathological features, as well as the prognosis of cancers, remains inconclusive. Therefore, a meta-analysis was performed to investigate the clinical significance of circ-ITCH in cancers by systematically summarizing all eligible literatures. Up to August 31, 2020, relevant articles were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane library, Embase, CNKI, and Wanfang databases. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and odds ratios (ORs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. A total of 1604 patients from 14 studies were included in this meta-analysis. The results showed that cancer patients with low circ-ITCH expression were more susceptible to develop lymph node metastasis (OR = 2.25, 95% CI: 1.67-3.02, p ≤ 0.01), larger tumor size (OR = 3.01, 95% CI: 2.01-4.52, p ≤ 0.01), advanced TNM stage (OR = 2.82, 95% CI: 1.92-4.14, p ≤ 0.01), and poor overall survival (OS) (HR = 2.45, 95% CI: 2.07-2.90, p ≤ 0.01, univariate analysis; HR = 2.69, 95% CI: 1.82-3.96, p ≤ 0.01, multivariate analysis). Thus, low circ-ITCH expression was significantly associated with aggressive clinicopathological features and unfavorable outcome in various cancers. Therefore, circ-ITCH may serve as a molecular therapy target and a prognostic marker in human cancers.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao-Dong Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no conflicts of interests in this work.
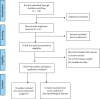
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circular RNA MYLK as a prognostic biomarker in patients with cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Sep;5(9):e1653. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1653. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 35701309 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulated circular RNA itchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase correlates with advanced pathologic T stage, high lymph node metastasis risk and poor survivals in prostate cancer patients.Cancer Biomark. 2019;26(1):41-50. doi: 10.3233/CBM-182111. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 31306101
-
Prognostic Role of Circular RNAs Expression in Bladder Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2020 Nov;24(11):692-700. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2020.0079. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2020. PMID: 33030352
-
Circular RNA ITCH suppresses metastasis of gastric cancer via regulating miR-199a-5p/Klotho axis.Cell Cycle. 2021 Mar-Mar;20(5-6):522-536. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1878327. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33499704 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA ITCH: A novel tumor suppressor in multiple cancers.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 1;254:117176. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117176. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31843532 Review.
Cited by
-
CircRNA ITCH: Insight Into Its Role and Clinical Application Prospect in Tumor and Non-Tumor Diseases.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 15;13:927541. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.927541. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35910224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Potential Use of Circular RNA for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 May 28;13:4251-4262. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S308809. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34093039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA MYLK as a prognostic biomarker in patients with cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Sep;5(9):e1653. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1653. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 35701309 Free PMC article.
-
Intelligent structure prediction and visualization analysis of non-coding RNA in osteosarcoma research.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 12;14:1255061. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1255061. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38532928 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

