Innate immune evasion mediated by picornaviral 3C protease: Possible lessons for coronaviral 3C-like protease?
- PMID: 33624382
- PMCID: PMC7883238
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2206
Innate immune evasion mediated by picornaviral 3C protease: Possible lessons for coronaviral 3C-like protease?
Abstract
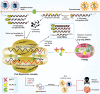
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 is the etiological agent of the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease-2019, a multi-organ disease that has triggered an unprecedented global health and economic crisis. The virally encoded 3C-like protease (3CLpro ), which is named after picornaviral 3C protease (3Cpro ) due to their similarities in substrate recognition and enzymatic activity, is essential for viral replication and has been considered as the primary drug target. However, information regarding the cellular substrates of 3CLpro and its interaction with the host remains scarce, though recent work has begun to shape our understanding more clearly. Here we summarized and compared the mechanisms by which picornaviruses and coronaviruses have evolved to evade innate immune surveillance, with a focus on the established role of 3Cpro in this process. Through this comparison, we hope to highlight the potential action and mechanisms that are conserved and shared between 3Cpro and 3CLpro . In this review, we also briefly discussed current advances in the development of broad-spectrum antivirals targeting both 3Cpro and 3CLpro .
Keywords: 3CLpro; 3Cpro; Covid-19; SARS-CoV-2; picornaviruses.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Picornaviral 3C protease inhibitors and the dual 3C protease/coronaviral 3C-like protease inhibitors.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2010 Jan;20(1):59-71. doi: 10.1517/13543770903460323. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2010. PMID: 20021285 Review.
-
The S2 Pocket Governs the Genus-Specific Substrate Selectivity of Coronavirus 3C-Like Protease.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(44):e2407766. doi: 10.1002/advs.202407766. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39377200 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of antiviral drug candidates targeting coronaviral 3C-like main proteases.FEBS J. 2021 Sep;288(17):5089-5121. doi: 10.1111/febs.15696. Epub 2021 Feb 1. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33400393 Review.
-
Identification of Host Cellular Protein Substrates of SARS-COV-2 Main Protease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 15;21(24):9523. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249523. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33333742 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting novel structural and functional features of coronavirus protease nsp5 (3CLpro, Mpro) in the age of COVID-19.J Gen Virol. 2021 Mar;102(3):001558. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001558. Epub 2021 Jan 28. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 33507143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of FRET and Stress Granule Dual-Based System to Screen for Viral 3C Protease Inhibitors.Molecules. 2023 Mar 28;28(7):3020. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073020. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049786 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral function and viral antagonism of the rapidly evolving dynein activating adaptor NINL.Elife. 2022 Oct 12;11:e81606. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81606. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36222652 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine Teschovirus 2 3Cpro Evades Host Antiviral Innate Immunity by Inhibiting the IFN-β Signaling Pathway.Microorganisms. 2025 May 26;13(6):1209. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061209. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572097 Free PMC article.
-
Picornavirus 3C Proteins Intervene in Host Cell Processes through Proteolysis and Interactions with RNA.Viruses. 2023 Dec 12;15(12):2413. doi: 10.3390/v15122413. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the origins of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Oct 13;15(1):81-118. doi: 10.1039/d3md00493g. eCollection 2024 Jan 25. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 38283212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wadman M, Couzin‐Frankel J, Kaiser J, Matacic C. A rampage through the body. Science. 2020;368:356‐360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

