Elinzanetant (NT-814), a Neurokinin 1,3 Receptor Antagonist, Reduces Estradiol and Progesterone in Healthy Women
- PMID: 33624806
- PMCID: PMC8277204
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab108
Elinzanetant (NT-814), a Neurokinin 1,3 Receptor Antagonist, Reduces Estradiol and Progesterone in Healthy Women
Abstract
Context: The ideal therapy for endometriosis (EM) and uterine fibroids (UFs) would suppress estrogenic drive to the endometrium and myometrium, while minimizing vasomotor symptoms and bone loss associated with current treatments. An integrated neurokinin-kisspeptin system involving substance P and neurokinin B acting at the neurokinin (NK) receptors 1 and 3, respectively, modulates reproductive hormone secretion and represents a therapeutic target.
Objective: This work aimed to assess the effects of the novel NK1,3 antagonist elinzanetant on reproductive hormone levels in healthy women.
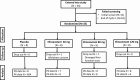
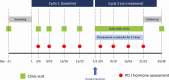
Methods: A randomized, single-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted in 33 women who attended for 2 consecutive menstrual cycles. In each cycle blood samples were taken on days 3 or 4, 9 or 10, 15 or 16, and 21 or 22 to measure serum reproductive hormones. In cycle 2, women were randomly assigned to receive once-daily oral elinzanetant 40, 80, 120 mg, or placebo (N = 8 or 9 per group).
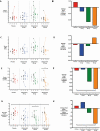
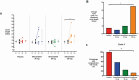
Results: Elinzanetant dose-dependently lowered serum luteinizing hormone, estradiol (120 mg median change across cycle: -141.4 pmol/L, P = .038), and luteal-phase progesterone (120 mg change from baseline on day 21 or 22: -19.400 nmol/L, P = .046). Elinzanetant 120 mg prolonged the cycle length by median of 7.0 days (P = .023). Elinzanetant reduced the proportion of women with a luteal-phase serum progesterone concentration greater than 30 nmol/L (a concentration consistent with ovulation) in a dose-related manner in cycle 2 (P = .002). Treatment did not produce vasomotor symptoms.
Conclusion: NK1,3 receptor antagonism with elinzanetant dose-dependently suppressed the reproductive axis in healthy women, with the 120-mg dose lowering estradiol to potentially ideal levels for UFs and EM. As such, elinzanetant may represent a novel therapy to manipulate reproductive hormone levels in women with hormone-driven disorders.
Keywords: GnRH; endometriosis; estradiol; neurokinin B; substance P; uterine fibroids.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Higher-level Modulation of GnRH Secretion: Progress Toward Next-generation Reproductive Treatments?J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jul 13;106(8):e3272-e3274. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab242. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33846737 No abstract available.
References
-
- Stewart EA, Cookson CL, Gandolfo RA, Schulze-Rath R. Epidemiology of uterine fibroids: a systematic review. BJOG. 2017;124(10):1501-1512. - PubMed
-
- Zondervan KT, Becker CM, Missmer SA. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(13):1244-1256. - PubMed
-
- Vercellini P, Viganò P, Somigliana E, Fedele L. Endometriosis: pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(5):261-275. - PubMed
-
- Noble LS, Simpson ER, Johns A, Bulun SE. Aromatase expression in endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(1):174-179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

