Effects of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Outcomes in Patients Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials
- PMID: 33625242
- PMCID: PMC8174267
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019463
Effects of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Outcomes in Patients Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background Recent studies have increasingly shown that sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors may have beneficial cardiovascular and metabolic effects in patients without diabetes mellitus. Hence, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes in patients without diabetes mellitus. Methods and Results Four electronic databases (PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and SCOPUS) were searched on August 30, 2020 for articles published from January 1, 2000 to August 30, 2020, for studies that examined the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes in patients without diabetes mellitus. A random-effects pairwise meta-analysis model was used to summarize the studies. A total of 8 randomized-controlled trials were included with a combined cohort of 5233 patients. In patients without diabetes mellitus, those with heart failure treated with SGLT2 inhibitors had a 20% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular deaths and heart failure hospitalizations, compared with those who were not treated (risk ratio, 0.78; P<0.001). We additionally found that treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors improved multiple metabolic indices. Patients on SGLT2 inhibitors had a reduction in body weight of -1.21 kg (P<0.001), body mass index of -0.47 kg/m2 (P<0.001), systolic blood pressure of -1.90 mm Hg (P=0.04), and fasting plasma glucose of -0.38 mmol/L (P=0.05), compared with those without. There were no between-group differences in NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide) levels, waist circumference, diastolic blood pressure, glycated hemoglobin, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and estimated glomerular filtration rates. Across our combined cohort of 5233 patients, hypoglycemia was reported in 22 patients. Conclusions SGLT2 inhibitors improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients without diabetes mellitus with heart failure. In patients without diabetes mellitus, SGLT2 inhibitors showed positive metabolic outcomes in weight and blood pressure control.
Keywords: nondiabetics; sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
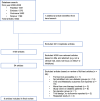


References
-
- Fitchett D, Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Hantel S, Salsali A, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE. Heart failure outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: results of the EMPA‐REG OUTCOME® trial. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:1526–1534. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv728. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoshida A, Matsubayashi Y, Nojima T, Suganami H, Abe T, Ishizawa M, Fujihara K, Tanaka S, Kaku K, Sone H. Attenuation of weight loss through improved antilipolytic effect in adipose tissue via the SGLT2 inhibitor tofogliflozin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:3647–3660. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2018-02254. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

