Pro-biomics: Omics Technologies To Unravel the Role of Probiotics in Health and Disease
- PMID: 33626128
- PMCID: PMC8483974
- DOI: 10.1093/advances/nmab014
Pro-biomics: Omics Technologies To Unravel the Role of Probiotics in Health and Disease
Abstract
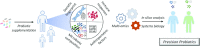
The comprehensive characterization of probiotic action has flourished during the past few decades, alongside the evolution of high-throughput, multiomics platforms. The integration of these platforms into probiotic animal and human studies has provided valuable insights into the holistic effects of probiotic supplementation on intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. Indeed, these methodologies have informed about global molecular changes induced in the host and residing commensals at multiple levels, providing a bulk of metagenomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data. The meaningful interpretation of generated data remains a challenge; however, the maturation of the field of systems biology and artificial intelligence has supported analysis of results. In this review article, we present current literature on the use of multiomics approaches in probiotic studies, we discuss current trends in probiotic research, and examine the possibility of tailor-made probiotic supplementation. Lastly, we delve deeper into newer technologies that have been developed in the last few years, such as single-cell multiomics analyses, and provide future directions for the maximization of probiotic efficacy.
Keywords: lactic acid bacteria; metabolomics; metagenomics; microbiome; probiotics; proteomics; transcriptomics.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Nutrition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring omics approaches in probiotics: Contemporary developments and prospective pathways.J Microbiol Methods. 2025 Jul;232-234:107135. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2025.107135. Epub 2025 Apr 19. J Microbiol Methods. 2025. PMID: 40258404 Review.
-
Lactobacillomics as a new notion in lactic acid bacteria research through omics integration.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 11;41(2):68. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04285-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39930163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating omics to unravel the stress-response mechanisms in probiotic bacteria: Approaches, challenges, and prospects.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Nov 2;57(16):3464-3471. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1136805. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26853094 Review.
-
Tackling probiotic and gut microbiota functionality through proteomics.J Proteomics. 2016 Sep 16;147:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.03.023. Epub 2016 Mar 18. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27003613 Review.
-
'Multi-omics' data integration: applications in probiotics studies.NPJ Sci Food. 2023 Jun 5;7(1):25. doi: 10.1038/s41538-023-00199-x. NPJ Sci Food. 2023. PMID: 37277356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Efficient Detection of Two Potential Probiotic Strains Using Whole Genome-Based Primers.Microorganisms. 2023 Oct 13;11(10):2553. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102553. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894211 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and applications of short-chain fatty acids derived from microbial fermentation of dietary fibers in human cancer.Front Nutr. 2023 Aug 8;10:1243390. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1243390. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37614742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges in the production and use of probiotics as therapeuticals in cancer treatment or prevention.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Dec 23;48(9-10):kuab052. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab052. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34427674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Milk and Its Derivatives as Sources of Components and Microorganisms with Health-Promoting Properties: Probiotics and Bioactive Peptides.Foods. 2024 Feb 16;13(4):601. doi: 10.3390/foods13040601. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38397577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Where Biology Meets Engineering: Scaling Up Microbial Nutraceuticals to Bridge Nutrition, Therapeutics, and Global Impact.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 2;13(3):566. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13030566. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40142459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) . Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. 2002; [Internet]. [cited 2020 May 22]. Available from: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/en/probiotic_guidelines.pdf
-
- Alard J, Lehrter V, Rhimi M, Mangin I, Peucelle V, Abraham AL, Mariadassou M, Maguin E, Waligora-Dupriet AJ, Pot Bet al. . Beneficial metabolic effects of selected probiotics on diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice are associated with improvement of dysbiotic gut microbiota. Environ Microbiol. 2016;18:1484–97. - PubMed
-
- So SS, Wan ML, El-Nezami H. Probiotics-mediated suppression of cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2017;29:62–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

