Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates bone erosion in rats that have collagen-induced arthritis via modulating NF-κB signalling to suppress osteoclastogenesis
- PMID: 33626293
- PMCID: PMC7906619
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1876100
Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates bone erosion in rats that have collagen-induced arthritis via modulating NF-κB signalling to suppress osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
Context: Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction (GSZD) is commonly used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but its mechanism is unclear.
Objective: To investigate the effect of GSZD on bone erosion in type II collagen (CII)-induced arthritis (CIA) in rats and to identify the underlying mechanism.
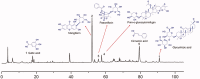
Materials and methods: The CIA model was prepared in male Wistar rats by two subcutaneous injections of CII, 1 mg/mL. Fifty CIA rats were randomized equally into the control group given saline daily, the positive group given saline daily and methotrexate 0.75 mg/kg once a week, and three GSZD-treated groups gavaged daily with 800, 1600 and 3200 mg/kg of GSZD for 21 days. GSZD effects were assessed by paw volume, arthritic severity index and histopathology. Cytokine levels were determined by ELISA. The effects of GSZD on RAW264.7 cells were evaluated by receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption assay. Expression of IκB-α and p65 was measured by Western blotting. Major components of GSZD were identified by HPLC.
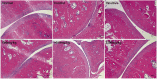
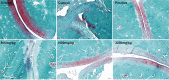
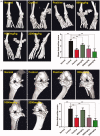
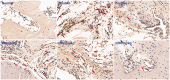
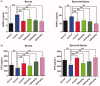
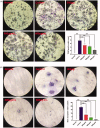
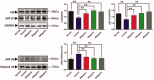
Results: Arthritis index score, paw volume and bone destruction score showed that GSZD improved inflammatory symptoms and reduced joint tissue erosion (p < 0.01). GSZD decreased RANKL, and the number of osteoclasts (OCs) in joint tissues (p < 0.01) and increased osteoprotegerin levels (p < 0.01). GSZD inhibited RANKL-induced RAW264.7 differentiation and reduced bone resorption by OCs. GSZD upregulated IκB (p < 0.01) and p65 (p < 0.01) in the cytoplasm and downregulated p65 (p < 0.01) in the cell nucleus.
Conclusions: Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction has an anti-RA effect, suggesting its possible use as a supplement and alternative drug therapy for RA.
Keywords: RANKL; Rheumatoid arthritis; osteoclast; osteoprotegerin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction possesses anti-arthritic effects on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats via suppression of inflammatory reactions, inhibition of invasion & migration and induction of apoptosis in synovial fibroblasts.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109367. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109367. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31545276
-
Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu granules attenuate bone destruction in mice with collagen-induced arthritis by promoting mitophagy of osteoclast precursors to inhibit osteoclastogenesis.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154967. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154967. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37490802
-
Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting inflammation by targeting SLPI.Phytomedicine. 2025 Apr;139:156471. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156471. Epub 2025 Feb 8. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39938174
-
Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation through inactivation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 30;283:114707. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114707. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34619319
-
Efficacy and tolerability of Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction in gout patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):1023-1034. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1823426. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 33205687 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting Therapeutic Windows for Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Sep;30(9):842-851. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3760-2. Epub 2024 May 16. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38753276 Review.
-
Advances in Experimental and Clinical Research of the Gouty Arthritis Treatment with Traditional Chinese Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 20;2021:8698232. doi: 10.1155/2021/8698232. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34721646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginkgetin attenuates bone loss in OVX mice by inhibiting the NF-κB/IκBα signaling pathway.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 10;12:e17722. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17722. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39006031 Free PMC article.
-
TCM and related active compounds in the treatment of gout: the regulation of signaling pathway and urate transporter.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 29;14:1275974. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1275974. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38094893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DS-Modified Paeoniflorin pH-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Macrophage Polarization in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 12;20:8967-8992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516434. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40671689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aletaha D, Smolen JS.. 2018. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA. 320(13):1360–1372. - PubMed
-
- Atkins G, Kostakis P, Vincent C, Farrugia AN, Houchins JP, Findlay DM, Evdokiou A, Zannettino AC.. 2006. RANK expression as a cell surface marker of human osteoclast precursors in peripheral blood, bone marrow, and giant cell tumors of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 21(9):1339–1349. - PubMed
-
- Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF.. 2007. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Protoc. 2(5):1269–1275. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
