Chromatin dysregulation associated with NSD1 mutation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 33626351
- PMCID: PMC8006058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108769
Chromatin dysregulation associated with NSD1 mutation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
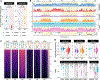
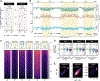
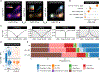
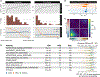
Chromatin dysregulation has emerged as an important mechanism of oncogenesis. To develop targeted treatments, it is important to understand the transcriptomic consequences of mutations in chromatin modifier genes. Recently, mutations in the histone methyltransferase gene nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1 (NSD1) have been identified in a subset of common and deadly head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs). Here, we use genome-wide approaches and genome editing to dissect the downstream effects of loss of NSD1 in HNSCC. We demonstrate that NSD1 mutations are responsible for loss of intergenic H3K36me2 domains, followed by loss of DNA methylation and gain of H3K27me3 in the affected genomic regions. In addition, those regions are enriched in cis-regulatory elements, and subsequent loss of H3K27ac correlates with reduced expression of their target genes. Our analysis identifies genes and pathways affected by the loss of NSD1 and paves the way to further understanding the interplay among chromatin modifications in cancer.
Keywords: cis-regulatory elements; epigenomics; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; histone H3 lysine 36 dimethylation; histone modifications; nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NSD1 mutation status determines metabolic inhibitor sensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by regulating mitochondrial respiration.J Pathol. 2025 Jul;266(3):306-321. doi: 10.1002/path.6430. Epub 2025 May 15. J Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40371884
-
Depletion of H3K36me2 recapitulates epigenomic and phenotypic changes induced by the H3.3K36M oncohistone mutation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 2;118(9):e2021795118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021795118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33619101 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Roles of the NSD Protein Methyltransferases in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 2;13(11):2013. doi: 10.3390/genes13112013. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired H3K36 methylation defines a subset of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Nat Genet. 2017 Feb;49(2):180-185. doi: 10.1038/ng.3757. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28067913 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Epigenetic Dysregulations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Dent Res. 2025 Mar;104(3):225-234. doi: 10.1177/00220345241297122. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Dent Res. 2025. PMID: 39698794 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of NSD2 causes dysregulation of synaptic genes and altered H3K36 dimethylation in mice.Front Genet. 2024 Feb 14;15:1308234. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1308234. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38419783 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of DNA Methylation Regulatory Function and Crosstalk with Histone Lysine Methylation.J Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 1;436(7):168394. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168394. Epub 2023 Dec 12. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38092287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NSD1 Mutations in Sotos Syndrome Induce Differential Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs, miR646 and Genes Controlling the G2/M Checkpoint.Life (Basel). 2022 Jul 2;12(7):988. doi: 10.3390/life12070988. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35888078 Free PMC article.
-
Histone lysine methyltransferase SMYD3 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via H3K4me3-mediated HMGA2 transcription.Clin Epigenetics. 2023 May 26;15(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01506-9. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37237385 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of function in NSD2 causes DNA methylation signature similar to that in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.Genet Med Open. 2024 Mar 14;2:101838. doi: 10.1016/j.gimo.2024.101838. eCollection 2024. Genet Med Open. 2024. PMID: 39669601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abugessaisa I, Noguchi S, Hasegawa A, Kondo A, Kawaji H, Carninci P, and Kasukawa T (2019). refTSS: a reference data set for human and mouse transcription start sites. J. Mol. Biol 431, 2407–2422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

