Antibody Response against SARS-CoV-2 and Seasonal Coronaviruses in Nonhospitalized COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 33627511
- PMCID: PMC8544894
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.01145-20
Antibody Response against SARS-CoV-2 and Seasonal Coronaviruses in Nonhospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
The majority of infections with SARS-CoV-2 are asymptomatic or mild without the necessity of hospitalization. It is of importance to reveal if these patients develop an antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 and to define which antibodies confer virus neutralization. We conducted a comprehensive serological survey of 49 patients with a mild course of disease and quantified neutralizing antibody responses against a clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolate employing human cells as targets. Four patients (8%), even though symptomatic, did not develop antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and two other patients (4%) were positive in only one of the six serological assays employed. For the remaining 88%, antibody response against the S protein correlated with serum neutralization whereas antibodies against the nucleocapsid were poor predictors of virus neutralization. None of the sera enhanced infection of human cells with SARS-CoV-2 at any dilution, arguing against antibody-dependent enhancement of infection in our system. Regarding neutralization, only six patients (12%) could be classified as high neutralizers. Furthermore, sera from several individuals with fairly high antibody levels had only poor neutralizing activity. In addition, employing a novel serological Western blot system to characterize antibody responses against seasonal coronaviruses, we found that antibodies against the seasonal coronavirus 229E might contribute to SARS-CoV-2 neutralization. Altogether, we show that there is a wide breadth of antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in patients that differentially correlate with virus neutralization. This highlights the difficulty to define reliable surrogate markers for immunity against SARS-CoV-2.IMPORTANCE There is strong interest in the nature of the neutralizing antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 in infected individuals. For vaccine development, it is especially important which antibodies confer protection against SARS-CoV-2, if there is a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of infection, and if there is cross-protection by antibodies directed against seasonal coronaviruses. We addressed these questions and found in accordance with other studies that neutralization is mediated mainly by antibodies directed against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in general and the receptor binding site in particular. In our test system, utilizing human cells for infection experiments, we did not detect ADE. However, using a novel diagnostic test we found that antibodies against the coronavirus 229E might be involved in cross-protection to SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE); neutralizing antibodies; seasonal coronaviruses.
Copyright © 2021 Ruetalo et al.
Figures
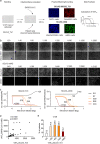
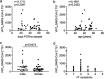
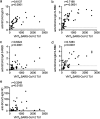
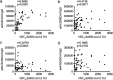
References
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. 2020. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382:727–733. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wolfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Muller MA, Niemeyer D, Jones TC, Vollmar P, Rothe C, Hoelscher M, Bleicker T, Brunink S, Schneider J, Ehmann R, Zwirglmaier K, Drosten C, Wendtner C. 2020. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 581:465–469. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lai CC, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Ko WC, Hsueh PR. 2020. Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality, and their association with country healthcare resources and economic status. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55:105946. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105946. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karagiannidis C, Mostert C, Hentschker C, Voshaar T, Malzahn J, Schillinger G, Klauber J, Janssens U, Marx G, Weber-Carstens S, Kluge S, Pfeifer M, Grabenhenrich L, Welte T, Busse R. 2020. Case characteristics, resource use, and outcomes of 10 021 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 920 German hospitals: an observational study. Lancet Respir Med 8:853–862. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30316-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
