Systematic evaluation of multiple qPCR platforms, NanoString and miRNA-Seq for microRNA biomarker discovery in human biofluids
- PMID: 33627690
- PMCID: PMC7904811
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83365-z
Systematic evaluation of multiple qPCR platforms, NanoString and miRNA-Seq for microRNA biomarker discovery in human biofluids
Abstract
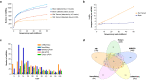
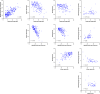
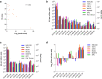
Aberrant miRNA expression has been associated with many diseases, and extracellular miRNAs that circulate in the bloodstream are remarkably stable. Recently, there has been growing interest in identifying cell-free circulating miRNAs that can serve as non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of disease or selection of treatment options. However, quantifying miRNA levels in biofluids is technically challenging due to their low abundance. Using reference samples, we performed a cross-platform evaluation in which miRNA profiling was performed on four different qPCR platforms (MiRXES, Qiagen, Applied Biosystems, Exiqon), nCounter technology (NanoString), and miRNA-Seq. Overall, our results suggest that using miRNA-Seq for discovery and targeted qPCR for validation is a rational strategy for miRNA biomarker development in clinical samples that involve limited amounts of biofluids.
Conflict of interest statement
L.Z. and R.Z. are shareholders and employees of MiRXES. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global and targeted circulating microRNA profiling of colorectal adenoma and colorectal cancer.Cancer. 2018 Feb 15;124(4):785-796. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31062. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29112225 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of MicroRNAs in the Biofluids of Livestock Species.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1733:65-77. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7601-0_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29435923
-
Identification of tubular injury microRNA biomarkers in urine: comparison of next-generation sequencing and qPCR-based profiling platforms.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 18;15(1):485. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-485. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24942259 Free PMC article.
-
Developing new TB biomarkers, are miRNA the answer?Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019 Sep;118:101860. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.101860. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019. PMID: 31472444 Review.
-
Human Circulating miRNAs Real-time qRT-PCR-based Analysis: An Overview of Endogenous Reference Genes Used for Data Normalization.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 5;20(18):4353. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184353. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31491899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liquid Biopsy and Circulating Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Precancerous and Cancerous Oral Lesions.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Aug 10;8(4):60. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8040060. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 36005828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of brain microRNAs in cognitive trajectory and Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Oct 30;148(1):59. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02818-7. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39477879 Free PMC article.
-
A one-pot isothermal Cas12-based assay for the sensitive detection of microRNAs.Nat Biomed Eng. 2023 Dec;7(12):1583-1601. doi: 10.1038/s41551-023-01033-1. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Nat Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 37106152 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Oncogene-Induced Senescence-Associated MicroRNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2906:189-213. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4426-3_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40082357
-
Machine-Learning-Based Single-Molecule Quantification of Circulating MicroRNA Mixtures.ACS Sens. 2023 Oct 27;8(10):3781-3792. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c01234. Epub 2023 Oct 4. ACS Sens. 2023. PMID: 37791886 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

