Transcriptional regulatory network for the establishment of CD8+ T cell exhaustion
- PMID: 33627794
- PMCID: PMC8080584
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-021-00568-0
Transcriptional regulatory network for the establishment of CD8+ T cell exhaustion
Abstract
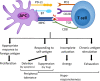
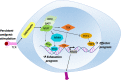
Chronic infection with persistent antigenic stimulation results in the generation of exhausted CD8+ T cells, which are considered defective effector CD8+ T cells, and thus compromises effective immune responses. However, recent studies have illustrated that exhausted CD8+ T cells may be purposely generated and maintained to provide mild immune responses against chronic infection or cancer, which can be safer over a long period of time than strong immune responses. Indeed, a specific population of exhausted CD8+ T cells that behaves similarly to self-renewing stem cells and provides a continuous supply of exhausted CD8+ T cells has been identified, indicating that this population can be considered progenitors of exhausted CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, several ground-breaking studies in the last few years have shed new light on the transcriptional regulatory network governing the generation and propagation of exhausted CD8+ T cells, which involves T cell receptor (TCR) signaling that leads to NFAT-TCF1 (nuclear factor of activated T cells-T cell factor 1) activity followed by activation of the TOX/NR4A axis. Elucidation of the intracellular signaling pathways will help to define the definitive developmental stages leading to exhausted CD8+ T cells, which can be exploited to advance our never-ending battle against cancer. This review will summarize the recent discoveries that have deepened our understanding of the exhaustion program of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
H.N. received honoraria and research funding from Ono Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, MSD and Bristol-Myers Squibb and research funding from Taiho Pharmaceutical, Daiichi-Sankyo, Kyowa Kirin, Zenyaku Kogyo, Oncolys BioPharma, Debiopharma, Asahi-Kasei, Sysmex, Fujifilm, SRL, Astellas Pharmaceutical, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and BD Japan outside of this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

