A mechanosensitive peri-arteriolar niche for osteogenesis and lymphopoiesis
- PMID: 33627868
- PMCID: PMC7979521
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03298-5
A mechanosensitive peri-arteriolar niche for osteogenesis and lymphopoiesis
Abstract
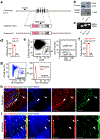
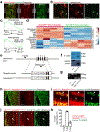
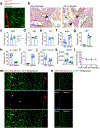
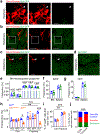
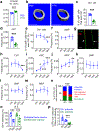
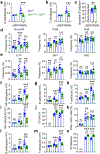
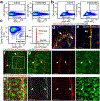
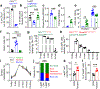
Stromal cells in adult bone marrow that express leptin receptor (LEPR) are a critical source of growth factors, including stem cell factor (SCF), for the maintenance of haematopoietic stem cells and early restricted progenitors1-6. LEPR+ cells are heterogeneous, including skeletal stem cells and osteogenic and adipogenic progenitors7-12, although few markers have been available to distinguish these subsets or to compare their functions. Here we show that expression of an osteogenic growth factor, osteolectin13,14, distinguishes peri-arteriolar LEPR+ cells poised to undergo osteogenesis from peri-sinusoidal LEPR+ cells poised to undergo adipogenesis (but retaining osteogenic potential). Peri-arteriolar LEPR+osteolectin+ cells are rapidly dividing, short-lived osteogenic progenitors that increase in number after fracture and are depleted during ageing. Deletion of Scf from adult osteolectin+ cells did not affect the maintenance of haematopoietic stem cells or most restricted progenitors but depleted common lymphoid progenitors, impairing lymphopoiesis, bacterial clearance, and survival after acute bacterial infection. Peri-arteriolar osteolectin+ cell maintenance required mechanical stimulation. Voluntary running increased, whereas hindlimb unloading decreased, the frequencies of peri-arteriolar osteolectin+ cells and common lymphoid progenitors. Deletion of the mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO1 from osteolectin+ cells depleted osteolectin+ cells and common lymphoid progenitors. These results show that a peri-arteriolar niche for osteogenesis and lymphopoiesis in bone marrow is maintained by mechanical stimulation and depleted during ageing.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Exercise generates immune cells in bone.Nature. 2021 Mar;591(7850):371-372. doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-00419-y. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33627859 No abstract available.
-
Osteolectin+ stromal cells: Mechanical stimulation improves bone regeneration and supports bacterial clearance after fracture.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jul 7;6(1):257. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00680-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34234107 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Runner's niche: multipurpose stromal cells maintained by exercise.Trends Immunol. 2021 Oct;42(10):841-843. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.08.007. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34479798
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

