Advances in Subcutaneous Delivery Systems of Biomacromolecular Agents for Diabetes Treatment
- PMID: 33628020
- PMCID: PMC7898203
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S283416
Advances in Subcutaneous Delivery Systems of Biomacromolecular Agents for Diabetes Treatment
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is a major threat to human health. Both its incidence and prevalence have been rising steadily over the past few decades. Biomacromolecular agents such as insulin and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists are commonly used hypoglycemic drugs that play important roles in the treatment of diabetes. However, their traditional frequent administration may cause numerous side effects, such as pain, infection or local tissue necrosis. To address these issues, many novel subcutaneous delivery systems have been developed in recent years. In this review, we survey recent developments in subcutaneous delivery systems of biomacromolecular hypoglycemic drugs, including sustained-release delivery systems and stimuli-responsive delivery systems, and summarize the advantages and limitations of these systems. Future opportunities and challenges are discussed as well.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists; insulin; stimuli-responsive; subcutaneous injection; sustained-release.
© 2021 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
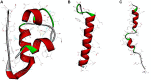
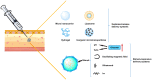

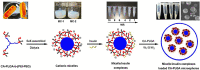
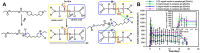




References
-
- Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, et al. Consensus statement by the American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - 2019 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2019;25(1):69–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

