A Comprehensive Review on Factors Influences Biogenesis, Functions, Therapeutic and Clinical Implications of Exosomes
- PMID: 33628021
- PMCID: PMC7898217
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S291956
A Comprehensive Review on Factors Influences Biogenesis, Functions, Therapeutic and Clinical Implications of Exosomes
Abstract
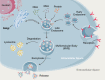
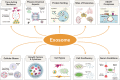
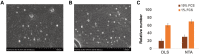
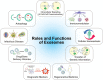
Exosomes are nanoscale-sized membrane vesicles secreted by almost all cell types into the extracellular environment upon fusion of multivesicular bodies and plasma membrane. Biogenesis of exosomes is a protein quality control mechanism, and once released, exosomes transmit signals to other cells. The applications of exosomes have increased immensely in biomedical fields owing to their cell-specific cargos that facilitate intercellular communications with neighboring cells through the transfer of biologically active compounds. The diverse constituents of exosomes reflect their cell of origin and their detection in biological fluids represents a diagnostic marker for various diseases. Exosome research is expanding rapidly due to the potential for clinical application to therapeutics and diagnosis. However, several aspects of exosome biology remain elusive. To discover the use of exosomes in the biomedical applications, we must better understand the basic molecular mechanisms underlying their biogenesis and function. In this comprehensive review, we describe factors involved in exosomes biogenesis and the role of exosomes in intercellular signaling and cell-cell communications, immune responses, cellular homeostasis, autophagy, and infectious diseases. In addition, we discuss the role of exosomes as diagnostic markers, and their therapeutic and clinical implications. Furthermore, we addressed the challenges and outstanding developments in exosome research, and discuss future perspectives.
Keywords: autophagy; biogenesis; cell-cell communication; cellular homeostasis; exosome; extracellular vesicle; function; immune response.
© 2021 Gurunathan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this work..
Figures

References
-
- Denzer K, Kleijmeer MJ, Heijnen HF, Stoorvogel W, Geuze HJ. Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 19):3365–3374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

