Insights into the actions of angiotensin-1 receptor (AT1R) inverse agonists: Perspectives and implications in COVID-19 treatment
- PMID: 33628162
- PMCID: PMC7898045
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2021-3412
Insights into the actions of angiotensin-1 receptor (AT1R) inverse agonists: Perspectives and implications in COVID-19 treatment
Abstract
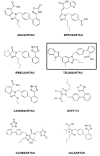
New coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) has caused chaos in health care systems. Clinical manifestations of COVID-19 are variable, with a complex pathophysiology and as yet no specific treatment. It has been suggested that the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system has a possible role in the severity of cases and the number of deaths. Our hypothesis is that drugs with inverse agonist effects to the angiotensin-1 receptor can be promising tools in the management of patients with COVID-19, possibly avoiding complications and the poor evolution in some cases. Any risk factors first need to be identified, and the most appropriate time to administer the drugs during the course of the infection also needs to be established. Several angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) have a favorable profile and are important candidates for the treatment of COVID-19. In this review we discussed a set of compounds with favorable profile for COVID-19 treatment, including azilsartan, candesartan, eprosartan, EXP3174, olmesartan, telmisartan, and valsartan. They are effective as inverse agonists and could reduce the "cytokine storm" and reducing oxidative stress. As COVID-19 disease has several evolution patterns, the effectiveness of ARB therapy would be related to infection "timing", patient risk factors, previous use of ARBs, and the specific molecular effects of an ARB. However, controlled studies are needed to identify whether ARBs are beneficial in the treatment of patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; angiotensin-converting enzyme; drugs; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Copyright © 2021 Heimfarth et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The place of ARBs in heart failure therapy: is aldosterone suppression the key?Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753944719868134. doi: 10.1177/1753944719868134. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31401939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of Death in Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19: A Retrospective Italian Cohort Study of 43,000 Patients.Drug Saf. 2020 Dec;43(12):1297-1308. doi: 10.1007/s40264-020-00994-5. Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 32852721 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockers in hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 2000 Apr;14 Suppl 1:S73-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1000991. J Hum Hypertens. 2000. PMID: 10854085 Review.
-
Efficacy of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Preventative Treatment of Episodic Migraine in Adults.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019 Sep 12;23(11):85. doi: 10.1007/s11916-019-0823-8. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019. PMID: 31515634
-
Current topics in angiotensin II type 1 receptor research: Focus on inverse agonism, receptor dimerization and biased agonism.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Sep;123:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.06.013. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28648738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
"Vision Loss" and COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vision (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;6(4):60. doi: 10.3390/vision6040060. Vision (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36278672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed HI, Mohamed EA. Candesartan and epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorate gentamicin-induced renal damage in rats through p38-MAPK and NF-κB pathways. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2019;33:e22254. - PubMed
-
- Akazawa H, Yasuda N, Komuro I. Mechanisms and functions of agonist-independent activation in the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;302:140–7. - PubMed
-
- Al-Majed AA, Bakheit AHH, Al-Muhsin A, Al-Kahtani HM, Abdelhameed AS. Azilsartan medoxomil. Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 2020;45:1–39. - PubMed
-
- Araújo AA, Araújo LS, Medeiros CACX, Leitão RFC, Brito GAC, Costa DVDS, et al. Protective effect of angiotensin II receptor blocker against oxidative stress and inflammation in an oral mucositis experimental model. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018;47:972–84. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
