Acupuncture at Back-Shu and Front-Mu Acupoints Prevents Gastric Ulcer by Regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF- κ B Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33628315
- PMCID: PMC7886517
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8214052
Acupuncture at Back-Shu and Front-Mu Acupoints Prevents Gastric Ulcer by Regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF- κ B Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the preventive effects of acupuncture at back-shu and front-mu acupoints on rats with restraint water-immersion stress (RWIS)-induced gastric ulcer.
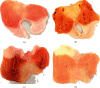
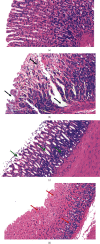
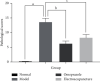
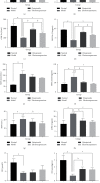
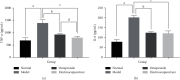
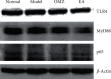
Methods: Thirty-six rats were randomly divided into four groups for 10 days of treatment as follows: the normal group received no treatment; the model group received RWIS-induced gastric ulcer; the omeprazole group was administered omeprazole orally every 2 days; and the electroacupuncture group received electroacupuncture at the RN12 and BL21 acupoints every 2 days. After 10 days of treatment, except for the normal group, all rats were induced with gastric ulcer by RWIS for 3 h. The ulcer index (UI), ulcer inhibition rate, and histopathological score were calculated. We determined the levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 in serum, and the activities of myeloperoxidase (MPO), malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), nitric oxide (NO), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in serum and gastric tissues. Protein expression of MyD88, nuclear factor (NF)-κB (p65), and toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 was quantified in gastric tissues.
Results: The electroacupuncture and omeprazole groups were equivalent in terms of UI, ulcer inhibition rate, and histopathological score. The serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were significantly lower in the electroacupuncture group compared with the omeprazole group (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, there were significant changes in the levels of NO, MPO, GSH-Px, and MDA in all other groups, while the expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB p65 in gastric tissue decreased significantly in the electroacupuncture group. The expression of TLR4 was substantially lower in the electroacupuncture group compared with the omeprazole group.
Conclusion: Acupuncture at back-shu and front-mu acupoints played a role in preventing gastric ulcer by inhibiting extracellular signals, stimulating kinases in serum and gastric tissues, and activating the inhibition of the TLR4 signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2021 Li Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Acupuncture preconditioning at "Zusanli"(ST36) and "Zhongwan"(CV12) prevents stress gastric ulcer by regulating the TLR4/MyD88/IκB signaling pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Mar 25;46(3):173-9. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200963. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 33798288 Chinese.
-
[Intervention mechanism of electroacupuncture in rats with ulcerative colitis: an analysis based on the Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020 Mar 25;45(3):180-7. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190358. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32202708 Chinese.
-
[Action mechanism of electroacupuncture at stomach meridian acupoints for oxidative damage in rats with gastric ulcer].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2016 Jun 12;36(6):617-621. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2016.06.017. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2016. PMID: 29231458 Chinese.
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture combined with Zhuang-medicine-thread moxibustion on silent information regulator-1/nuclear factor κB signaling pathway in gastric antrum of diabetic gastroparesis rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Oct 25;46(10):837-44. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200942. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34698457 Chinese.
-
Effect of Electroacupuncture in "Zusanli" and "Kunlun" Acupoints on TLR4 Signaling Pathway of Adjuvant Arthritis Rats.Am J Ther. 2018 May/Jun;25(3):e314-e319. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000477. Am J Ther. 2018. PMID: 27574922
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Insights Into Electroacupuncture Using Different Acupoint Combinations to Repair Mucosal Inflammatory Injury Induced in a Rat Model of Gastric Ulcer.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 11;18:3399-3417. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S504930. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40093956 Free PMC article.
-
NMR-based metabonomics reveals the dynamic effect of electro-acupuncture on central nervous system in gastric mucosal lesions (GML) rats.Chin Med. 2022 Mar 21;17(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00593-9. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35313919 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of TLR9, MyD88, and NF-κB p65 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 13;2022:6830366. doi: 10.1155/2022/6830366. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9875013. doi: 10.1155/2023/9875013. PMID: 35733626 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Management of a Patient With Premenstrual Syndrome Using Acupuncture, Supplements, and Meditation: A Case Report.J Chiropr Med. 2023 Sep;22(3):222-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Chiropr Med. 2023. PMID: 37644997 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq Reveals Protective Mechanisms of Mongolian Medicine Molor-Dabos-4 on Acute Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;13(10):1740. doi: 10.3390/genes13101740. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292625 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

