Effect of Duyun Compound Green Tea on Gut Microbiota Diversity in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice Revealed by Illumina High-Throughput Sequencing
- PMID: 33628318
- PMCID: PMC7886516
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8832554
Effect of Duyun Compound Green Tea on Gut Microbiota Diversity in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice Revealed by Illumina High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
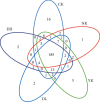
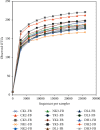
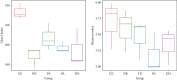
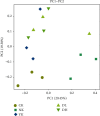
Intake of a high-fat diet (HFD) is closely related to disorders of the intestinal microbiota, which plays a key role in the pathogenesis of obesity. Duyun compound green tea, an ancient Chinese drink, is widely consumed to reduce weight, although the mechanism is not clear. In this study, 50 mice were randomly divided into 5 groups: normal control group (CK), HFD model control group (NK), positive control group with medicine (YK), low-dose compound tea group (DL), and high-dose compound tea group (DH). After 4 weeks of intervention, the feces of mice were taken under sterile conditions and evaluated using Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology. The results showed that the diversity of intestinal microbiota was the highest in the CK group, the lowest in the NK group, and relatively increased in the compound tea treatment group. Second, there were differences in intestinal microbiota in each group, among which the beneficial bacteria in the intestinal tract of the CK group were higher than those in the other groups, while the beneficial bacteria in each compound tea treatment group were more abundant than those in the NK group, in which harmful bacteria in the intestinal tract were found to be the highest. These results suggest that compounds in tea may be able to attenuate imbalances of intestinal microbiota induced by poor diet, acting as a therapeutic agent in obesity or other diseases associated with gut dysbiosis.
Copyright © 2021 Caibi Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Compound Fu brick tea modifies the intestinal microbiome composition in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice.Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Aug 31;8(10):5508-5520. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1850. eCollection 2020 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33133553 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics improve gut microbiota dysbiosis in obese mice fed a high-fat or high-sucrose diet.Nutrition. 2019 Apr;60:175-184. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Nutrition. 2019. PMID: 30611080
-
Fuzhuan Brick Tea Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Associated Metabolic Disorders by Shaping Gut Microbiota.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Dec 11;67(49):13589-13604. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05833. Epub 2019 Nov 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31735025
-
Effects of Tea Seed Oil Extracted by Different Refining Temperatures on the Intestinal Microbiota of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Foods. 2024 Jul 26;13(15):2352. doi: 10.3390/foods13152352. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123544 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation effect of tea consumption on gut microbiota.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;104(3):981-987. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10306-2. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31853562 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Bacillus coagulans on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Intestinal Microbiota of the Juvenile Fourfinger Threadfin (Eleutheronema tetradactylum).Animals (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;15(4):515. doi: 10.3390/ani15040515. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peck S. C., Denger K., Burrichter A., Irwin S. M., Balskus E. P., Schleheck D. A glycyl radical enzyme enables hydrogen sulfide production by the human intestinal bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2019;116(8):3171–3176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815661116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

